Instruction 157n on budget accounting of fixed assets. We work correctly: all instructions on budget accounting. New edition of accounts
Amendments are being made to Instruction No. 157n (O. Zabolonkova)
Date of article posting: 06/13/2015
Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 29, 2014 N 89n “On amendments to the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 N 157n” “On approval of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), bodies” is being registered with the Ministry of Justice. local self-government, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions and the Instructions for its application" (hereinafter - Order No. 89n, Instruction No. 157n). Let's consider the main provisions of this document.
Changes in the Unified Chart of Accounts
Let us recall that Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 157n contains the Unified Chart of Accounts. The following amendments have been made to it:
- account names have been changed:
|
Account number |
Old name |
New name |
|
Cash in the institution's accounts with a credit institution |
Funds of the institution in a credit institution |
|
|
Calculations for property damage |
Calculations for damage and other income |
|
|
Calculations for other property |
Calculations for other income |
|
|
Accepted obligations |
Liabilities |
- account excluded:
- new accounts have been introduced:
|
Account number |
Name |
|
Balance accounts |
|
|
Calculations for unidentified receipts |
|
|
Cost compensation calculations |
|
|
Calculations of forced seizure amounts |
|
|
Calculations for other income |
|
|
VAT calculations on advances received |
|
|
VAT calculations on purchased material assets, works, services |
|
|
Reserves for future expenses (by type of expense) |
|
|
Authorization for other subsequent years (outside the planning period) |
|
|
Obligations accepted |
|
|
Deferred liabilities |
|
|
Off-balance sheet accounts |
|
|
Material assets issued for personal use to employees (employees) |
|
|
Calculations for the fulfillment of monetary obligations through third parties |
|
Changes in general accounting provisions
Requirements for accounting documents. Clause 3 of Instruction No. 157n lists the requirements for accounting. By Order No. 89n they are expanded by the following provisions:
Primary accounting documents received as a result of internal control of completed facts of economic life for registration of the data contained in them in accounting registers are accepted for accounting, on the assumption of proper preparation of primary accounting documents on completed facts of economic life by the persons responsible for their registration;
Accounting data and the reporting of accounting entities generated on their basis are formed taking into account the materiality of the facts of economic life that have had or may have an impact on the financial condition, cash flow or results of operations of the institution and took place in the period between the reporting date and the date of signing the accounting (financial) ) reporting for the reporting year (hereinafter referred to as the event after the reporting date).
Based on clause 9 of Instruction No. 157n (new edition), timely and high-quality execution of primary accounting documents, their transfer within the established time frame for reflection in accounting, as well as the reliability of the data contained in them are ensured by persons those responsible for registration of the fact of economic life and (or) those who signed these documents. Order No. 89n introduced an addition to this paragraph, according to which the person entrusted with maintaining accounting records and the person with whom an agreement for the provision of services (agreement on the transfer of powers) for maintaining accounting (budget) records was concluded are not responsible for the compliance of the drawn up other persons of primary accounting documents to accomplished facts of economic life.
The requirements for the forms of accounting registers have been supplemented with new provisions. In particular, it is established that registers, the forms of which are not unified, are established by the accounting entity as part of the formation of its accounting policies and must contain the following mandatory details:
Register name;
Name of the accounting entity that compiled the register;
The start date and end date of maintaining the register and (or) the period for which the register was compiled;
Chronological and (or) systematic grouping of accounting objects;
The amount of monetary and (or) natural measurement of accounting objects, indicating the unit of measurement;
Names of positions of persons responsible for maintaining the register;
Signatures of the persons responsible for maintaining the register, indicating their last names and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
In addition, a provision has been introduced clarifying that corrections are reflected in the electronic accounting register by persons responsible for maintaining the register in the manner prescribed by clause 18 of Instruction No. 157n, with records confirmed by certificates.
Automation of accounting. The following requirements are imposed on the automation of accounting, taking into account the changes made by Order No. 89n to clause 19 of Instruction No. 157n.
With comprehensive automation of accounting, information about accounting objects is generated in the databases of the software package used. The formation of accounting registers is carried out in the form of an electronic register, and in the absence of technical capabilities - on paper.
Accounting registers on paper, if there is no possibility of storing them in the form of electronic documents signed with an electronic signature, and (or) the need to ensure their storage on paper, are formed at the frequency established as part of the formation of accounting policies by the subject of accounting, but not less frequently than the frequency established for the preparation and presentation by the accounting entity of accounting (financial) statements generated on the basis of data from the relevant accounting registers.
As before, when transferring accounting registers to paper (generating machine diagrams of accounting registers), it is allowed to differ between the output form of the document (machine diagram) and the approved form of the document, provided that the details and indicators of the output form of the document (machine diagram) contain the mandatory details and indicators of the corresponding accounting registers.
Inventory. It is important to note the following point. According to the amendments made to clause 20 of Instruction No. 157n, the inventory of property, financial assets and liabilities is carried out by the accounting entity in the manner established by him as part of the formation of accounting policies taking into account the provisions of the legislation of the Russian Federation. Previously, it was necessary to conduct an inventory in accordance with the requirements of the Ministry of Finance.
Changes in accounting for non-financial assets
Fixed assets. Let us recall: clause 27 of Instruction No. 157n establishes that the book value of non-financial assets is their original cost, taking into account its changes.
Order No. 89n introduced an addition, according to which the result of repair work on an object of fixed assets that does not change its value (including the replacement of elements in a complex object of fixed assets (in a complex of structurally articulated objects that constitute a single whole)) is subject to reflection in the accounting register - inventory card of the corresponding fixed asset object - by making entries about the changes made without being reflected in the accounting accounts.
In addition, the features of accounting for fixed assets under conservation are explained. In particular, clause 38 of Instruction No. 157n as amended by Order No. 89n establishes that the mothballing of a fixed asset object for a period of more than three months (re-mothballing) is formalized by a primary accounting document - an act on conservation (re-mothballing) of fixed assets, containing information about the accounting object ( name, inventory number of the object, its original (book) value, amount of accrued depreciation), as well as information about the reasons for conservation and the period of conservation.
An object of fixed assets that is under conservation continues to be listed on the corresponding balance sheet accounts of the working chart of accounts of the institution as an object of fixed assets.
Reflection of conservation (re-preservation) of an object of fixed assets for a period of more than three months is reflected by making a record of conservation (re-preservation) of the object in the inventory card of the accounting object, without reflecting account 0 101 00 000 “Fixed assets” in the corresponding analytical accounts.
Clause 45 of Instruction No. 157n provides a definition of the unit of accounting for a fixed asset - an inventory item.
The provisions of Order No. 89n further clarify that:
Separate premises of buildings that have different functional purposes, and are also independent objects of property rights, are accounted for as independent inventory objects of fixed assets;
The road environment (technical means of organizing traffic, including road signs, fencing, markings, guide devices, traffic lights, automated traffic control systems, lighting networks, landscaping and small architectural forms) is taken into account as part of the road, unless otherwise established by the procedure for maintaining the register property of the relevant public legal entity;
In cases provided for by the accounting policies of accounting entities, aircraft engines are accounted for as independent inventory items of fixed assets.
Land is a non-produced asset. According to paragraphs 23, 71 of Instruction No. 157n (as amended by Order No. 89n), land plots used by institutions on the right of permanent (perpetual) use (including those located under real estate) must be accounted for as part of non-financial assets on the balance sheet account 103 00 “Non-produced assets” on the basis of a document (certificate) confirming the right to use the land plot. Land plots are accounted for at their cadastral value (the value specified in the document for the right to use a land plot located outside the territory of the Russian Federation).
Let us recall that currently Instruction No. 157n requires such land plots to be accounted for in off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use.” Therefore, they now need to be transferred from this account to the balance sheet account.
Changes in accounting for financial assets
The institution's funds are on the way. By virtue of clause 162 of Instruction No. 157n (as amended by Order No. 89n), account 201 03 is intended to account for operations on the movement of funds of the institution in the currency of the Russian Federation and in foreign currency in transit. For accounting purposes and Instruction No. 157n, funds in transit are funds transferred to an institution, credited on more than one business day, as well as funds transferred from one account of an institution to another account, including when carrying out transactions using (debit) bank cards, provided that funds are transferred (credited) on more than one business day.
As you can see, the new edition of this paragraph is due to the use of bank cards by institutions in financial activities.
Calculations with accountable persons. The changes affected accountable amounts issued in foreign currency. Paragraph 215 of Instruction No. 157n establishes that the accounting of debts of accountable persons for advances issued in foreign currencies is simultaneously carried out in the corresponding foreign currency and in the ruble equivalent on the date of issuance of funds for reporting.
Order No. 89n introduces the following additions to this paragraph. Revaluation of settlements for advances issued in foreign currencies is carried out on the date of operations to return previously made payments in the corresponding foreign currency.
Revaluation of debt under accepted obligations in foreign currencies is carried out on the date of transactions to pay the obligation in foreign currency and on the reporting date (on the date of formation of the accounting register).
In this case, positive (negative) exchange rate differences that arose when calculating the ruble equivalent are attributed to the increase (decrease) in settlements for accepted obligations in foreign currency, with exchange rate differences being attributed to the financial result of the current financial year from the revaluation of assets.
Calculations for damage and other income. Order No. 89n added that account 209 00 is used, among other things, to account for settlements for amounts of advance payments not returned by the counterparty in the event of termination of contracts (other agreements), in particular by court decision, for amounts of debt of accountable persons not returned in a timely manner (not withheld from wages), on the amounts of debt for unworked vacation days when an employee is dismissed before the end of the working year for which he has already received annual paid leave, on the amounts of excessive payments made, on the amounts of forced withdrawal, including compensation for damages in in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, in the event of insured events, as well as in the amount of damage caused as a result of the actions (inaction) of officials of the organization (clause 220 of Instruction No. 157n (as amended by Order No. 89n)).
In connection with the introduction of new analytical groups for account 209 00, paragraph 221 of Instruction No. 157n in the new edition provides the following explanations. Grouping of calculations for damage and other income is carried out by income groups and analytical groups of the synthetic account of the accounting object:
30 "Calculations for cost compensation";
40 “Calculations for forced seizure amounts”;
70 “Calculations for damage to non-financial assets”;
80 "Calculations for other income."
It is clarified that the accounts for settlements of damage and other income take into account:
Calculations of the amounts owed by former employees to the institution for unworked vacation days upon their dismissal before the end of the working year for which they have already received annual paid leave;
Calculations for the amounts of advance payments subject to reimbursement by counterparties in the event of termination, including by a court decision, of state (municipal) agreements (contracts), other agreements (agreements) under which payments were previously made by the institution;
Calculations of amounts owed by accountable persons that were not returned in a timely manner (not withheld from wages), including in the event of a challenge to the deductions;
Calculations of the amount of damage subject to compensation by a court decision in the form of compensation for expenses associated with legal proceedings (payment of legal costs);
Calculations for other damages, as well as other income arising in the course of the economic activities of the institution, not reflected in accounts 205 00 “Calculations for income”.
Note! Order No. 89n introduced a new definition of the amount of damage. In particular, it has been established that when determining the amount of damage caused by shortages and thefts, one should proceed from the current replacement cost(previously - market) material assets on the day the damage was discovered. Under current replacement cost refers to the amount of money that necessary for recovery specified assets.
Calculations for tax deductions for VAT. As already mentioned at the beginning of the article, Order No. 89 introduced a new account 210 10 “Calculations for tax deductions for VAT”. Grouping of calculations for it is carried out in the context of analytical groups of the synthetic account of the accounting object:
1 "Calculations for VAT on advances received";
2 "Calculations for VAT on acquired material assets, works, services."
Paragraph 224 of Instruction No. 157n (as amended) establishes that the account is intended to account for:
Calculations of value added tax amounts on received advance payments for the upcoming sale of non-financial assets (works, services) within the framework of the activities of the institution, subject to value added tax in the manner prescribed by the tax legislation of the Russian Federation;
Calculations for amounts of value added tax presented by suppliers (contractors) for supplied non-financial assets, work performed, services rendered, accrued and paid by the institution as a tax agent in cases provided for by the tax legislation of the Russian Federation.
Changes in accounting for off-balance sheet accounts
Account 02 "Material assets accepted for storage." Order No. 89n, paragraph 335 of Instruction No. 157n is supplemented by a rule according to which this account also records property in respect of which a decision has been made to write off (cessation of operation), including due to physical or moral wear and tear and the impossibility (inexpediency) of it further use until its dismantling (disposal, destruction).
Account 03 "Strict reporting forms". In accordance with the amendments made to paragraph 337 of Instruction No. 157n, the list of forms classified as strict reporting forms can be established by the institution as part of the formation of accounting policies.
Account 04 "Debt of insolvent debtors". Write-off of debt from off-balance sheet accounting is carried out on the basis of a decision of the institution’s commission on the receipt and disposal of assets in the presence of documents confirming the termination of the obligation by the death (liquidation) of the debtor, as well as upon expiration of the period for the possible resumption of the debt collection procedure in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 339 of Instructions No. 157n (new edition)).
Account 09 "Spare parts for vehicles issued to replace worn-out ones." When a vehicle is disposed of, spare parts installed on it and accounted for in an off-balance sheet account are written off from off-balance sheet accounting (clause 349 of Instruction No. 157n (as amended)).
Account 27 "Material assets issued for personal use to employees (employees)." The account was introduced by Order No. 89n. It is intended to account for property issued by an institution for personal use to employees for the performance of their official (official) duties, in order to ensure control over its safety, intended use and movement (clause 385 of Instruction No. 157n).
Acceptance of property items for accounting is carried out on the basis of the primary accounting document at book value.
The disposal of property items from off-balance sheet accounting is carried out on the basis of the primary accounting document at the cost at which the objects were previously accepted for off-balance sheet accounting.
Analytical accounting of the account is carried out in a card of quantitative and total accounting of material assets in the context of users of the property, its location, by type of property, its quantity and value.
Account 30 "Settlements for the fulfillment of monetary obligations through third parties." Another new off-balance sheet account is intended for accounting for settlements for the fulfillment of monetary obligations through third parties (when paying pensions, benefits through branches of the Russian Post, paying agents) (clause 387 of Instruction No. 157n).
Analytical accounting for this account is maintained in a multi-graph card and (or) in a card for accounting for funds and settlements in the context of monetary obligations by type of payment of budget funds or other types of payments.
Paragraph 2 of Order No. 89n establishes that this Order is applied when forming indicators of accounting objects on the last day of the reporting period of 2014, unless otherwise provided by the accounting policy of the institution. The transition to the application of accounting policies, taking into account the provisions of the new Order regarding the work plan of institutions, is carried out according to the organizational and technical readiness of accounting entities.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 N 157n (as amended on December 28, 2018) “On approval of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, government bodies...
MINISTRY OF FINANCE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
ORDER
ON APPROVAL OF A UNIFIED CHART OF ACCOUNTS
FOR GOVERNMENT BODIES (STATE
BODIES), LOCAL GOVERNMENT BODIES, BODIES
MANAGEMENT OF STATE EXTRABUDGETARY FUNDS,
STATE ACADEMIES OF SCIENCES, STATE
(MUNICIPAL) INSTITUTIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS
ON ITS APPLICATION
Based on Article 165 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 1998, No. 31, Art. 3823; 2005, No. 1, Art. 8; 2006, No. 1, Art. 8; 2007, No. 18, Art. 2117; No. 45, Art. 5424), paragraphs 4 and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 7, 2004 No. 185 “Issues of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2004, No. 15, Art. 1478; No. 49, Art. 4908; 2007, N 45, Art. 5491; 2008, N 5, Art. 411) and in order to establish a uniform procedure for maintaining accounting records by public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences , state (municipal) institutions I order:
1. Approve the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to this Order.
2. Approve the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to this Order.
3.1. This order applies to:
A) State Atomic Energy Corporation "Rosatom", State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos" in terms of maintaining budgetary accounting of economic facts that arise in the exercise of powers of the main manager of budget funds, the recipient of budget funds, the chief administrator of budget revenues and the administrator of budget revenues, as well as when transferring, free of charge, on the basis of agreements, its powers as a state customer to conclude and execute government contracts on behalf of the Russian Federation, including within the framework of the state defense order, on behalf of these corporations when making budgetary investments in capital construction projects of state property of the Russian Federation (with the exception of powers related to the introduction into operation of state-owned objects of the Russian Federation in the prescribed manner) and for the acquisition of real estate objects into the state ownership of the Russian Federation by federal state unitary enterprises, in respect of which the specified corporations exercise on behalf of the Russian Federation the powers of the owner of the property, in compliance with budget legislation;
B) state (municipal) unitary enterprises in terms of maintaining budgetary accounting of the facts of economic life that arise during the exercise, on the basis of agreements, of the powers of the state (municipal) customer to conclude and execute on behalf of the corresponding public legal entity state (municipal) contracts on behalf of public authorities (state bodies), management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, local governments that are state (municipal) customers, when making budget investments in state (municipal) property and receiving budget investments in capital construction projects of state (municipal) property and (or) for the acquisition of state (municipal) property in the manner established for recipients of budget funds.
(see text in the previous edition)
4. To recognize as invalid:
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2008 N 148n “On approval of the Instructions for Budget Accounting” (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on February 12, 2009, registration number 13309; Rossiyskaya Gazeta, 2009, March 6);
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 3, 2009 N 69n "On introducing amendments to the Instructions on budget accounting approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2008 N 148n" (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on August 13, 2009 , registration number 14524; Rossiyskaya Gazeta, 2009, September 2);
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2009 N 152n "On introducing amendments to the Instructions on budget accounting approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2008 N 148n" (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on February 4, 2010 , registration number 16247; Rossiyskaya Gazeta, 2010, February 19).
By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2017 No. 148n (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 148n), further changes are made to Instruction No. 157n . Currently, this document is posted on the website of the financial department and is being registered with the Ministry of Justice. Let's look at what innovations that are relevant for educational institutions and which it has prepared for accountants.
Unified chart of accounts.
The Unified Chart of Accounts has undergone minor changes. For example, account 206 61 “Calculations for advances on pensions, benefits and payments for pension, social and health insurance of the population” has been excluded.
The word “pensions” was removed from the name of account 206 63; now it is called: “Calculations for advances on benefits paid by organizations in the public administration sector.”
General provisions.
Paragraph 3 of Instruction No. 157n provides recommendations that institutions should take into account when maintaining accounting records. In particular, para. 12 of this paragraph establishes that accounting must reflect information that does not contain significant errors and distortions, allowing its users to rely on it as truthful. For the purposes of Instruction No. 157n, material information is information, the omission or distortion of which may affect the economic decision of the founders of the institution (users of information), made on the basis of accounting data and (or) accounting (financial) statements of the accounting entity.
Order No. 148n introduces additions according to which the reliability of the financial statements is not affected by the presence of errors and (or) distortions in the indicators of the financial statements of institutions that do not affect the economic decision of their founders made on the basis of data from such statements and do not form the indicators necessary for the assessment compliance by institutions with the conditions for receiving subsidies.
In addition, a new concept has been introduced - the “principle of prudence”. It means the following: when maintaining accounting records, an institution must ensure priority recognition in accounting of expenses and liabilities over the recognition of possible income and assets.
Error correction.
In accordance with clause 18 of Instruction No. 157n, additional accounting entries for correcting errors, as well as corrections using the “red reversal” method, are drawn up with a primary accounting document drawn up by the institution - a certificate (f. 0504833). The specified document must contain:
information on the rationale for making corrections;
name of the accounting register (transaction journal) being corrected, its number (if available);
the period for which it was compiled;
the period in which errors were identified (this requirement was introduced by Order No. 148n).
Also, Order No. 148n established that accounting records for correcting errors of previous years are subject to separation in accounting (budget) accounting and financial statements.
Inventory.
Order No. 148n in paragraph 20 of Instruction No. 157n, regulating the inventory of property, financial assets and liabilities, made clarifying amendments, according to which other accounting objects are also subject to inventory, including off-balance sheet accounts, and is carried out for the purpose of drawing up an annual report ( earlier - before compilation).
Working chart of accounts.
The procedure for creating a working chart of accounts is prescribed in clause 21 of Instruction No. 157n. Order No. 148n clarified that the formation of a working chart of accounts (in the 1st - 17th digits of the account number - the corresponding codes of the budget classification of the Russian Federation (their components), in the 24th - 26th digits - KOSGU) is carried out taking into account the provisions provided for by the instructions for application of the chart of accounts of budgetary accounting, chart of accounts of treasury accounting, chart of accounts of accounting of budgetary institutions, chart of accounts of accounting of autonomous institutions.
Non-financial assets.
Paragraph 22 of Instruction No. 157n contains information about what assets are accounted for in the accounts of the “Non-financial assets” section. Order No. 148n clarifies that these accounts must also take into account assets transferred for lease, free use, in trust, as well as property that is the subject of a concession agreement.
Let us remind you: according to clause 27 of Instruction No. 157n, actual investments in an object of non-financial assets in the amount of costs for its modernization, additional equipment, reconstruction, including elements of restoration, technical re-equipment, reflected in the accounting of the organization exercising the powers of the recipient of budget funds, are transferred to the balance sheet holder of the object , in respect of which modernization, additional equipment, reconstruction, including elements of restoration, technical re-equipment have been carried out (completed) in order to attribute the amount of the specified actual investments to increase the initial (book) value of this object. According to the changes made to this paragraph by Order No. 148n, such transfer of investment is carried out on the basis of a notice (f. 504805) with the attachment of documents confirming the volume of capital investments made for completed work (stages of work).
As you know, the unit of accounting for fixed assets is an inventory object. Order No. 148n specifies that inventory items of fixed assets are accepted for accounting in accordance with the specifications established in clause 45 of Instruction No. 157n and taking into account the grouping of fixed assets objects provided for by the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets. This change is of a corrective nature due to the cancellation of the action from 01/01/2017 OK 013-94 “All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets”, approved by Decree of the State Standard of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1994 No. 359, in connection with the publication of the Order of Rosstandart dated December 12, 2014 No. 2018-st , which adopted OK 013-2014 “All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets” (OKOF) (SNA 2008).
Intangible assets.
Paragraph 56 of Instruction No. 157n provides a definition of intangible assets subject to accounting on account 102 00. The condition according to which objects of non-financial assets, when classified as intangible assets, must be repeatedly and (or) constantly used in the activities of the institution with the right of operational management is excluded from it.
The formation rules initial cost changes were also made to intangible assets. In particular, don't turn on at the indicated price:
registration fees, state fees, patent fees and other similar payments made in connection with the acquisition (receipt) of exclusive (property) rights to intangible assets;
remunerations paid to the intermediary organization through which the intangible asset was acquired;
amounts paid by the institution for information and consulting services related to the acquisition (creation) of intangible assets;
amounts paid for the performance of work or provision of services when creating an intangible asset in accordance with agreements (state (municipal) contracts), including under author's order agreements (author's agreements), agreements for the performance of research, development, and technological work (if creation of an intangible asset).
Expenses that are not included in the amount of actual investments have also been adjusted, in particular, it has been clarified that this amount does not include expenses for research, development and technological work, provided by the institution under agreements (contracts) . Before the amendments were made, expenses for work of previous reporting periods that were recognized as income and expenses were not included.
Income calculations.
Paragraph 199 of Instruction No. 157n provides a grouping of calculations on account 205 00 “Calculations for income” by analytical groups of the synthetic account of accounting objects.
According to the changes made by Order No. 148n, the account containing the analytical code of the synthetic account group “Calculations for insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance” is taken into account for compulsory social insurance; before the changes were made, budget revenues were taken into account.
Calculations for advances issued.
Let us remind you that account 206 00 “Settlements for advances issued” takes into account settlements for advance payments provided by the institution in accordance with the terms of concluded agreements (contracts), agreements (except for advances issued to accountable persons) (clause 202 of Instruction No. 157n).
In particular, advances for wages and accruals for wage payments should be reflected in account 206, containing the analytical code of the synthetic account group “Calculations for advances for wages and accruals for wage payments” and the corresponding analytical code for the type of synthetic account of financial assets . By Order No. 148n, an analytical code for the type of synthetic account 1 “Payroll calculations” was added to this group code, that is, 206 11. It should be noted that in the unified chart of accounts given in Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 157n, there is such an account; it turns out that this amendment affected only the text part of Appendix 2 of Instruction No. 157n.
In account 206, which contains the analytical code of the synthetic account group “Calculations for advances on social security”, the analytical code of type 1 “Calculations for advances on pensions, benefits and payments for pension, social and medical insurance of the population” is excluded. At the beginning of the article it was already mentioned that account 206 61 was excluded from the unified chart of accounts.
Authorization of expenses.
Paragraph 312 of Instruction No. 157n establishes that indicators (balances) for the corresponding analytical accounts for accounting for budget allocations, limits on budget obligations, fulfilled monetary obligations and approved budget (planned, forecast) assignments for income (receipts), expenses ( payments) of the current financial year.
Here are the features of transferring indicators (balances) for authorizing expenses generated in the reporting financial year for the first, second years following the current (next) financial year to analytical accounts for authorizing expenses:
indicators for authorization of the first year following the current one (the next financial year) - to the authorization accounts of the current financial year;
indicators for authorization of the second year following the current one (the first year following the reporting year) - to the authorization accounts of the first year following the current one (the next financial year);
indicators for the authorization of the second year following the next one - to the authorization accounts of the second year following the current one (the first year following the next one).
From the changes made by Order No. 148n to this paragraph, it follows that not only balances, but also turnover are subject to transfer.
Let's summarize. In the unified chart of accounts, the name of account 20663 was adjusted, account 20661 was excluded. The amendments made to Instruction No. 157n clarify the procedure for reflecting errors found in accounting registers, the procedure for accounting for individual items of non-financial assets, in particular intangible assets. The features of calculations for income based on advances issued have also been adjusted.
It should be added that Order No. 148n introduced changes to the requirements for accepting for accounting and determining the estimated value of the values of the State Fund (State Fund of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation), but in the article they are not considered as irrelevant for educational institutions.
What is Order No. 157n (instructions on budget accounting) as amended (2019)? This is a unified structure for the formation of synthetic and analytical accounts, designed to distribute the facts of the financial and economic activities of the entity by assets and liabilities. In addition to the procedure for generating accounting accounts, the document contains detailed explanations of the rules for the application and execution of records - accounting transactions.
Instruction 157n on budget accounting in 2019 as amended, the text was last adjusted on 03/31/2018 by a separate Order No. 64n.
Who should apply:
- state-owned, BU and AU;
- government agencies and local governments;
- financial authorities and the Treasury;
- extra-budgetary funds of all levels.
Current document: instruction 157n on budget accounting in 2019 with changes (download).
Memo on instructions 157n on budget accounting in 2019 with changes

For all types of government institutions, separate regulations are provided that regulate the features of the formation of a unified chart of accounts for a specific type.
Thus, for public sector employees, a unified chart of accounts is approved by Order Instruction 174n on budget accounting in 2019, as amended. Full name - Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n.
Current order - No. 174n (instructions for budget accounting) with amendments (2019)

For autonomous institutions - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 23, 2010 No. 183n (as amended on March 31, 2018)

For government agencies and other recipients of budget funds - 162n (instructions for budget accounting) as amended (2019) (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n)

Features of application
Please note that the use of all accounting accounts named in the regulatory documents is not necessary. Each institution independently determines the list of synthetic and analytical accounts that are required to maintain full-fledged accounting. The working chart of accounts is approved in the accounting policy of the organization.
Let us remind you that government agencies have the right to apply additional detail to existing accounting accounts. This can be established by the founder or a higher-ranking manager of the BS.
Primary and accounting documents
52n (instructions for budget accounting), as amended (2019), regulates the forms of primary documentation and accounting registers to reflect the economic facts of the institution’s activities. The document is valid for all types of government institutions (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n (as amended on November 17, 2017)).

The document states:
- list of forms of primary documents and accounting journals;
- unified documentation forms;
- methodological recommendations for filling out forms.
Let us note that institutions have the right to independently develop (modify, change or create) other forms of primary and accounting documentation that take into account the specific features of the organization’s activities. Such norms are enshrined in Law No. 402-FZ. However, it is better to coordinate such decisions with higher-level RBS. In other words, instruction 52n on budget accounting in 2019, as amended, is not mandatory for use.
Budget reporting
The full list of reporting forms for public sector employees is also regulated by special instructions of the Ministry of Finance - in the instructions on budget accounting for budgetary institutions in 2019. The regulatory document establishes:
- full composition of reporting forms;
- frequency of delivery;
- reporting procedure;
- Features of reflecting accounting operations in reporting forms.
However, officials differentiated the composition and procedure for preparing financial statements by type of institution.
For recipients of budget funds (treasury government agencies, state and municipal authorities, financial authorities and the Treasury, as well as extra-budgetary funds), Instruction No. 191n applies (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2010 No. 191n (as amended on November 30, 2018)).

AU and BU are required to prepare financial statements taking into account 33n (instructions for budget accounting) as amended (2019) (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 25, 2011 No. 33n (as amended on November 30, 2018)).

Please remember that deadlines are set individually. Instruction 33n on budget accounting in 2019, as amended, does not regulate the deadlines. That is, specific deadlines for the provision of monthly, quarterly and annual accounting reports are set by higher-level RBS or the founder.
Documents useful in the work of an accountant
In addition to key instructions on accounting in budgetary institutions in 2019, accountants use other regulations. For example, Order No. 173n (instructions for budget accounting), as amended (2019), regulates the procedure for generating information, as well as the rules for exchanging this information with the financial committee authorities for maintaining a register of contracts concluded as a result of procurement.

But the procedure for returning funds to the federal budget of the state is established in instruction 152n on budget accounting in 2019, as amended.
O. Grishakova
expert of the magazine “Autonomous Institutions: Accounting and Taxation”
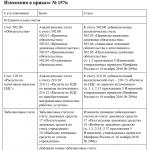
On May 8, Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 31, 2018 No. 64n came into force, which amended Instruction No. 157n. These amendments must be applied when developing accounting policies for 2018. In this article we will provide an overview of the main innovations in the instructions itself.
The need to adjust Instruction No. 157n is due to certain federal standards for public sector organizations that entered into force in 2018 and innovations in the application of KOSGU, namely:
– GHS “Conceptual Framework”;
– GHS “Fixed Assets”; – GHS “Impairment of Assets”;
– by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2017 No. 255n, dated November 29, 2017 No. 209n.
Instruction No. 157n now explicitly states that it is applied simultaneously with the GHS “Conceptual Framework”, and the text of Instruction No. 157n has been supplemented with references to the above-mentioned federal standards.
The main changes affected the sections “General Provisions” and “Non-Financial Assets”; we will discuss them further.
Section "General Provisions"
This section excludes certain provisions that duplicate the rules of the GHS “Conceptual Framework”, including provisions on the preparation and submission of primary accounting documents and on the procedure for conducting an inventory of assets and liabilities.
Some provisions are set out in a new edition.
In paragraph 3 of Instruction No. 157n it is clarified that when maintaining accounting records, the accounting entity ensures priority recognition in accounting of expenses and liabilities over the recognition of possible income and assets, reflecting these accounting objects according to the most conservative estimates - without overstating assets and (or) income and not underestimating liabilities and (or) expenses (principle of prudence). This principle was provided for earlier, but there was no explanation of what is meant by it.
In paragraph 6 of Instruction No. 157n, the composition of the accounting policy has been adjusted. In fact, the update of this paragraph did not make significant changes. The only thing that can be highlighted is the rules of document flow, which should also be part of the accounting policy. Previously, a similar provision was contained in paragraph 9 (it was deleted).
Paragraph 14 of Instruction No. 157n now clarifies that the storage of primary (consolidated) accounting documents, accounting registers and accounting (financial) statements is organized by the head of the accounting entity and (or) the head of the centralized accounting department.
In addition, the same paragraph now contains a provision that when there is a change in the head of the accounting entity and (or) the chief accountant or other official entrusted with accounting, the transfer of the institution’s accounting documents is ensured. The procedure for transferring these documents must be provided for in the accounting policy, and in the case of transferring the powers of accounting under a contract (agreement) to centralized accounting - by such contract (agreement).
Section "Non-financial assets"
Lease objects are classified as non-financial assets. In paragraph 22 of Instruction No. 157n, an addition was made that the accounts for accounting for non-financial assets also take into account property received under lease agreements, free use, for trust management, and lease accounting objects related to fixed assets for accounting purposes.
The rules for determining the initial cost of non-financial assets have been adjusted. Corresponding amendments have been made to clauses 23 – 26 of Instruction No. 157n.
The initial cost of non-financial assets is recognized as the amount of actual costs when acquiring as a result of exchange transactions, construction or production (creation) of non-financial assets, taking into account the amounts of value added tax presented to the institution by suppliers and (or) contractors (except for the acquisition, construction and production of non-financial assets within activities of an institution subject to VAT), unless otherwise provided by Instruction No. 157n.
The initial (actual) cost of objects of non-financial assets received under agreements providing for the fulfillment of obligations (payment) in non-monetary means is recognized as the value of assets transferred or to be transferred by the institution in order to fulfill obligations under the agreement. The value of items transferred or to be transferred by an institution is determined at their fair value based on the price at which, in comparable circumstances, the institution would normally determine the value of similar items (at which similar non-financial assets would be purchased in comparable circumstances). If it is impossible to establish the fair value of assets transferred or to be transferred by the institution, the value of non-financial assets received by the institution under these agreements is determined based on the residual (book) value of the asset transferred in exchange. If data on the residual value of the asset transferred in exchange is for some reason unavailable, or on the date of transfer the residual value of the asset transferred in exchange is zero, such an object of non-financial assets is reflected by the institution in a conditional valuation: one object - one ruble.
The initial (actual) cost of objects of non-financial assets received by an institution under a non-exchange transaction (free of charge, including under a gift agreement) is their current estimated value on the date of acceptance for accounting, recognized as the fair value of these objects, increased by the cost of services related to their delivery, registration and bringing them into a condition suitable for use.
The current estimated value of a non-financial asset is determined by the market price method based on data on transactions with a similar or similar asset made without deferred payment, and is made in the amount of funds required for the sale (purchase) of these assets on the date of acceptance for accounting.
The current estimated value for the purpose of accepting a non-financial asset for accounting is determined on the basis of the price in effect on the date of acceptance for accounting (capitalization) of property received free of charge for this or a similar type of property. Information about the current price must be confirmed by documents, and in cases where documentary confirmation is not possible - by expert means.
When determining the current estimated value for the purpose of accepting a non-financial asset for accounting by the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets created in the institution on an ongoing basis, data on prices for similar material assets received in writing from manufacturing organizations are used; information on the price level available from state statistics bodies, as well as in the media and specialized literature, expert opinions (including experts recruited on a voluntary basis to work in the commission on the receipt and disposal of assets) on the cost of individual (similar) objects non-financial assets.
If data on prices for similar or similar material assets is unavailable for any reason, in order to ensure continuous accounting and complete reflection of accomplished facts of economic activity, the current estimated value is recognized in a conditional valuation equal to one ruble. At the same time, the specified material assets that meet the criteria for asset recognition are reflected by the accounting entity on balance sheet accounts in a conditional valuation: one object - one ruble.
After receiving data on prices for similar or similar tangible assets for an object of a non-financial asset (tangible asset), reflected as of the date of recognition in the conditional valuation, the accounting entity’s commission revises the book (fair) value of such an object.
The initial (book) value of lease accounting objects is determined in accordance with the GHS “Lease”.
Impairment of an asset results in a change in its carrying amount. Clause 27 of Instruction No. 157n names cases when the book value of non-financial assets changes. These include:
– completion;
– retrofitting;
– reconstruction;
- technical re-equipment;
– modernization;
– partial liquidation (dismantling);
– revaluation of non-financial assets;
– depreciation.
According to the amendments, this paragraph was supplemented with the last position.
Reflection of non-financial assets upon their alienation. Due to the additions made to clause 28 of Instruction No. 157n, non-financial assets, with the exception of finished products and goods intended for disposal not in favor of public sector organizations, are reflected in accounting at fair value determined by the market price method.
The result of revaluation to fair value, determined by the market price method, is reflected in accounting and disclosed in the accounting (financial) statements separately as part of the financial result of the current period.
Features of accounting for non-financial assets received through non-exchange transactions. According to the updated clause 32 of Instruction No. 157n, tangible objects of non-financial assets received by an institution through non-exchange transactions, before they are recognized as part of balance sheet accounting items (assets), are taken into account by the accounting entity in the corresponding off-balance sheet accounts at the cost indicated upon their receipt, and in cases where there is no such – in conditional valuation: one object – one ruble.
Material objects of non-financial assets in use by the institution, provided by the balance sheet holder in the performance of the functions assigned to him for organizational and technical support of other institutions (authorities) created by the owner of the property, and for the maintenance of state (municipal) property, are taken into account by the subject of accounting on the corresponding off-balance sheet accounts according to the value indicated upon their receipt (transfer).
Accounting for objects that do not bring economic benefits. In accordance with the amendments made to clauses 34, 35 of Instruction No. 157n, objects of non-financial assets that do not bring economic benefits to the institution, do not have useful potential, in respect of which it is also not envisaged to receive them in the future, including in connection with full or partial loss of consumer properties, technical potential (physical or moral wear and tear), are taken into account in off-balance sheet accounts. Termination of recognition of an object as an asset is carried out on the basis of a decision of the permanent commission for the receipt and disposal of assets, drawn up in a supporting document (primary (consolidated) accounting document). Information about such objects is subject to disclosure in accounting (financial) statements.
To account for the institution’s material assets that do not meet the asset criteria, account 02 “Tangible assets in storage” is used.
The grouping of analytical codes of the synthetic account has been adjusted. According to clause 37 of Instruction No. 157n, accounting for non-financial assets is carried out according to the following analytical groups of the synthetic account of the Unified Chart of Accounts:
1. By property:
10 “Real estate of the institution”;
20 “Especially valuable movable property of the institution”;
30 “Other movable property of the institution”;
40 “Rights to use assets”;
50 “Non-financial assets that make up the treasury”;
90 “Property in concession”.
2. According to the costs of production of finished products, works, services:
60 “Cost of finished products, works, services”;
70 “Overhead costs of production of finished products, works, services”;
80 “General business expenses”.
Previously, group 40 reflected leasing objects, now - the rights to use assets (in relation to property leased by the institution). Previously, group 90 was intended to account for distribution costs, but is now used to account for property in a concession.
Changes in fixed asset accounting
In Instruction No. 157n, some provisions that duplicate the GHS standards “Fixed Assets” have been abolished. Certain paragraphs have been supplemented with new provisions.
Biological resources. A new paragraph has been introduced into paragraph 45 of Instruction No. 157n, clarifying that the “Biological Resources” accounting group includes service dogs, perennial plantings, horses and other objects of animal (live animals) and plant origin (trees and other perennial crops, for example, orchards, vineyards, other plantations), repeatedly producing products whose natural growth and restoration are under the direct control of the accounting entity.
The procedure for assigning an inventory number has been supplemented with new provisions. According to the amendments made to clause 46 of Instruction No. 157n, each inventory item of real estate, as well as an inventory item of movable property, with the exception of items worth up to 10,000 rubles. inclusive, and objects of the library collection, regardless of their value, are assigned a unique inventory serial number, regardless of whether it is in operation, in reserve or in conservation.
Each fixed asset object included in a complex of fixed asset objects, recognized for accounting purposes as a single inventory object, is assigned an internal serial inventory number of the complex of objects, formed as a combination of the inventory number of the complex of objects and the serial number of the object included in the complex.
Objects of fixed assets that have a unique number that uniquely identifies them as an individually defined thing (for example, a cadastral number, a state (registration) identification mark (number) of a vehicle, a serial number of a manufactured weapon) are assigned an inventory number without applying it to the object .
When reclassifying fixed assets, the inventory number does not change (including if the accounting group of non-financial assets is changed, when objects listed on off-balance sheet accounts are accepted for balance sheet accounting). Corresponding amendments have been made to clause 47 of Instruction No. 157n.
Accounting for inseparable improvements to property objects that are objects of accounting for operating leases (formation of their inventory numbers) is carried out by ensuring the identification of each inventory object with the corresponding right to use the asset (clause 49 of Instruction No. 157n).
Accounting for fixed assets worth up to 10,000 rubles. In accordance with the updated paragraph 50 of Instruction No. 157n, the initial cost of movable property objects put into operation (transferred) that are fixed assets worth up to 10,000 rubles. inclusive, with the exception of library collection objects, is written off from the balance sheet while simultaneously reflecting the objects on an off-balance sheet account.
In order to ensure proper control over the movement of fixed assets in operation by the institution worth up to 10,000 rubles. inclusive, with the exception of library collection objects and real estate objects, off-balance sheet account 21 “Fixed assets in operation” is intended.
Disposal of fixed assets from accounting. Due to the additions made to clause 52 of Instruction No. 157n, to reflect in accounting transactions on the disposal of fixed assets from off-balance sheet account 02 “Tangible assets in storage” or from the corresponding analytical accounts 101 00 000 “Fixed assets”, acts are accepted if available on them, approval of the decision to write off fixed assets in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, with the owner of the property (with the body exercising the functions and powers of the founder) and the approving inscription of the head of the institution.
Reflection in the accounting records of the disposal of a fixed asset item from off-balance sheet account 02 before the decision on the write-off (disposal) of the said object is approved in the prescribed manner and the implementation of the measures provided for in the write-off act is not allowed.
The grouping of fixed assets is brought into compliance with the GHS standards “Fixed assets”.
Changes in accounting for non-produced assets
According to the additions made to clause 71 of Instruction No. 157n, land plots used by institutions on the right of permanent (perpetual) use (including those located under real estate), as well as land plots for which property is not demarcated, are involved by authorized authorities ( local government bodies) into economic circulation, are taken into account in the corresponding analytical accounting account account 103 00 000 “Non-produced assets” on the basis of a document (certificate) confirming the right to use the land plot, at their cadastral value (the value specified in the document for the right to use the land plot located outside the territory of the Russian Federation), and in the absence of a cadastral value of a land plot - at a value calculated based on the lowest cadastral value per square meter of a land plot bordering the object of registration, and if it is impossible to determine such a value - in a conditional valuation: one square meter - one ruble.
Depreciation of non-financial assets
In accordance with the amendments made to clause 92 of Instruction No. 157n, depreciation for fixed assets is calculated in accordance with the GHS “Fixed Assets”.
Depreciation of the right to use assets is calculated in accordance with the GHS “Rent”.
The depreciation procedure for intangible assets has also been adjusted (clause 93 of Instruction No. 157n):
– for objects worth up to 100,000 rubles. inclusive, depreciation is charged in the amount of 100% of the book value when the object is registered;
– for objects worth over 100,000 rubles. depreciation is accrued in accordance with depreciation rates calculated in accordance with the established procedure.
Rights to use assets
Accounting for the rights to use assets (operating lease objects) is carried out in accordance with the GHS “Lease” and the newly introduced clauses 151.1 – 151.4 of Instruction No. 157n. For these purposes, account 111 00 000 is now designated in the Unified Chart of Accounts. Analytical accounting is carried out on it for objects received for use and for rights holders (lessors) in the context of contracts, locations of property received for use, as well as persons responsible for safety of such objects and (or) their intended use.
Rights to use assets are accounted for according to the corresponding analytical code of the type of synthetic account of the accounting object:
– 41 “Rights to use residential premises”;
– 42 “Rights to use non-residential premises (buildings and structures)”;
– 44 “Rights to use machinery and equipment”;
– 45 “Rights to use vehicles”;
– 46 “Rights to use industrial and household equipment”;
– 47 “Rights to use biological resources”;
– 48 “Rights to use other fixed assets.”
Accounting for transactions on disposal (reclassification) of the right to use assets is kept in the journal of transactions on disposal and transfer of non-financial assets.
Impairment of non-financial assets
Impairment of non-financial assets is reflected in accounting in accordance with the GHS “Impairment of Assets” and new clauses 151.5 – 151.7 of Instruction No. 157n. According to the changes made, to account for the decrease in the value of assets due to their impairment, account 114,00,000 is used for the corresponding analytical groups of the synthetic account of the accounting object:
– 10 “Depreciation of the institution’s real estate”;
– 20 “Depreciation of particularly valuable movable property of an institution”;
– 30 “Depreciation of other movable property of the institution”;
– 40 “Impairment of rights to use assets.”
Accounting for asset impairment transactions is also maintained in the journal of transactions on disposal and transfer of non-financial assets.
Summarizing the above, we note that changes were also made to the sections “Financial assets”, “Financial result”, they affected the procedure for applying new accounts for income (in connection with the detailing of KOSGU) and for accounting for financial results (in terms of accounts to reflect corrections of errors previous years). Adjustments have also been made to the procedure for using off-balance sheet accounts.
Corresponding amendments have also been made to instruction No. 183n. Accountants of state (municipal) institutions have been waiting for these changes since the beginning of the year. And now in accounting it is necessary to reflect operations on the transition to a new procedure for accounting for operations on fixed assets and leases, as well as on the income and expenses of the institution.
Let us recall that the Ministry of Finance in letters dated December 15, 2017 No. 02-07-07/84237, dated December 13, 2017 No. 02-07-07/83464, No. 02-07-07/83463 gave clarifications on the transitional provisions for the application of the GHS “Basic funds" and "Rent" (including correspondence accounts), but it was not possible to fully apply them in practice until amendments were made to the main instructions.
It should be noted that at the time of preparation of this material there were no explanations on how to transfer balances to new accounts. Perhaps the Ministry of Finance will prepare additional recommendations in the near future.
Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n.
Approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2016 No. 256n.
Approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2016 No. 257n.
Approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2016 No. 258n.
Approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2016 No. 259n.
The accounting of income on new accounts is described in detail in the article by G. Selishcheva “Accounting for income according to the new rules.”