Net profit of the enterprise. Formula. Methods of analysis and purposes of use. Tax profit in the balance sheet is a line How to find profit on the balance sheet
- equality of assets and liabilities;
- a significant increase in the balance sheet currency, which characterizes the growth of business volumes;
- “bad” growth in warehouse inventories and the volume of supplier invoices payable;
- the appearance of a short-term loan; Apparently, the company was unable to provide servicing of the increased working capital from its own funds;
- a fairly large volume of retained earnings, which increased shareholders' equity in 2010;
- significant increase in other accounts payable; Most likely, these are unshipped products based on received advance payments...
- accounts receivable in 2010 are significantly lower than the volume of accounts payable; this means that the company will not be able to pay suppliers until it sells a significant portion of its inventory.
Interesting? This is how much information can be gleaned from the balance sheet.
The main criterion for calculating the efficiency of capital is its payback
The income structure on the balance sheet consists of 3 main elements:
- profit (damage) from the sale of industrial products;
- profit (damage) from other sales;
- profit (loss) on non-operating transactions;
Let's look at the composition of each of them. Elements of balance sheet profit Income from the sale of industrial goods Profit from the sale of industrial products is the total economic result of the sale of basic industrial goods (services) produced in accordance with the law or the company's charter, minus damages for the creation of these industrial goods or services. This type of income in a company determines and shows the main indicative production activities, and is considered the most important component of balance sheet profit.
Balance sheet profit and the formula for calculating it
Having saddled themselves with cash, they begin to think about the management income statement. The pinnacle of financial management is the analysis of assets [using the balance sheet] (Fig. 5). Rice. 5. Hierarchy of financial instruments of Russian management Due to the above, Russian managers, as a rule, have a poor understanding of the balance sheet, and do not know how to compile it or “read” it... In accounting, the balance sheet is the main document.
Accountants are very good at preparing a balance sheet and understand its importance. Unfortunately, these differences result in managers and accountants speaking different languages, which further reinforces managers' disregard for the balance sheet. In modern practice, the balance sheet is depicted not in a horizontal form (assets on the left, and capital on the right), but in a vertical form - assets at the top, capital at the bottom.
Book profit: formula
Analysis of the basic and chain indices of the amount of balance sheet profit excludes the influence on the conclusions obtained on the basis of calculations, the size and dynamics of taxes payable (which will happen when comparing the size of net profit), which is important for management and planning. Calculation of the indicator “balance sheet profit” Balance sheet profit for a period characterizes as such the final financial result from all activities of the organization that had a monetary value. For book profit, the formula for calculating the indicator for a period is as follows: Thus, book profit is the company’s net income after paying all production, administrative and commercial expenses for the period under review.
A positive difference means that the organization has a profit, a negative difference means a balance sheet loss for the period under review.
How is revenue reflected on the balance sheet?
The most important circumstances for constantly increasing the profit of an organization and depending on its activities can be considered:
- an increase in the volume of goods produced that does not contradict the contractual terms;
- reducing damage to production;
- increasing the quality of manufactured goods;
- increase in assortment;
- increasing the efficiency of using production assets;
- increasing labor productivity;
Changes in the stability of state regulation, the impact of natural, geographical, transport and other conditions are of the nature of factors independent of the activities of the enterprise.
Balance sheet profit formula
Non-operating operations may include:
- fines;
- fines;
- payment for violation of the terms of the contract between enterprises;
- other income;
- amounts from outstanding accounts receivable from previous periods;
- funds from foreign exchange transactions in cooperation with foreign enterprises;
- income from holding funds in accounts;
In addition, non-operating operations can include finances of authorized share participation in other companies, or interest income from founder shares. How to calculate book profit? The unconditional performance of a company's production is determined by its final economic indicators. The most important of these is the profit indicator.
Balance sheet profit is the most important determining financial result of the economic activity of an enterprise.
IMPORTANT! If a company receives revenue at the cash desk, situations cannot be ruled out when the following limits may be exceeded:
- cash settlements between legal entities (directive of the Bank of Russia dated October 7, 2013 No. 3073-U);
- balance of cash in the cash desk (instruction of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U).
Such violations may be punishable under Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For more information about the rules that must be followed when working with cash proceeds, read the material “Cash discipline and responsibility for its violation.” The connection between revenue and this balance sheet item can be traced in detail by studying another accounting report - on cash flow.
But the information from the balance sheet already makes you think. 3rd section of the balance sheet and revenue Unlike other lines and sections of the balance sheet, this section is directly related to the report in which revenue appears.
The company's total income line on the balance sheet
Attention
It also shows other income minus other expenses. Next, the tax burden is applied to the balance sheet profit. It is worth remembering that insurance premiums are included in the cost price as part of wages and are deducted from the balance sheet profit.
Pre-tax profits are subject to income tax of 20% and other federal and territorial taxes and duties. In some cases, an enterprise takes into account losses from previous periods within the balance sheet profit. Profit before tax shows the financial performance of a company. The indicator takes into account all income and expenses for core and additional activities. The importance of this type of profit lies in the fact that it bears the tax burden. (25 votes, average: 4.30 out of 5) Loading...
In the following sections we will dwell in more detail on the analysis of the financial and economic activities of companies based on the balance sheet and profit and loss account. See also:
- Basics of Corporate Finance
- Balance, its structure and basic concepts
- Gains and losses report
- Main financial indicators
- Financial leverage effect, balanced growth
- Classical and neoclassical cost accounting
- Behavior of costs when activity volumes change
- Break-even analysis
- Using cost analysis to make management decisions
- Cost calculation
- ABC method: process-by-process costing
Balance sheet currency – the amount (total) for all component accounts of the balance sheet.
The two sides of a balance sheet are just two different ways of representing the same amount of money, i.e. information about where the money came from to the company and where it went (Fig. 2). In the future, we will very often use this property of the balance sheet - equality of assets and liabilities. Rice. 2. Balance sheet, as information about the sources of income and directions of use of capital Assets (Fig. 3) are divided into non-current (fixed assets, intangible assets, long-term financial investments) and current (inventories, accounts receivable, cash on account and in cash register, others).
All commercial organizations strive to obtain maximum profit, since it is its value that determines how effective and successful the company's policy is. Profit before tax is precisely the indicator the calculation of which is necessary to assess the real result of economic activity.
Let's discuss what profit before tax is and in which accounting documents it is present, and also consider the formula for calculating it and a clear example.
Profit before tax is...
The phrase speaks for itself: profit is the total positive result of the company’s activities; pre-tax – before the moment of payment of income tax. The point is that you need to determine the figure by which income exceeds expenses excluding tax. Although, of course, no one is immune from a situation when there is no profit, but there is a loss (of course, its magnitude should also be clarified).
Calculation of profit (loss) before tax is necessary for several important reasons:
- Any organization needs to calculate the amount of net profit in order to, if necessary, distribute it among participants, and this is not feasible without calculating the indicator in question.
- Profit before tax allows you to determine the tax base and calculate the tax that needs to be paid. Of course, today any company can easily find out everything about its debts (for example, this is done on several Internet portals), but you shouldn’t let it get to that point.
- If a company suffers a misfortune in the form of a loss, then it is important to know the amount of compensation.
- Rationalization, that is, a smooth reduction in future costs, is possible only if the company has the opportunity to fully evaluate the results of its business activities.
- Based on the calculated profit before tax, sales can subsequently be determined, which is sometimes called an indicator of the organization's pricing policy, since it shows the efficiency of operations.
- The indicator is often used to calculate various ratios illustrating the state of affairs of the company.
Important: accounting for profit before tax is necessarily reflected in the company’s accounting documents, namely in the Financial Results Report. If a positive calculation result is obtained, then the amount is profit; when the figure is negative, the company faces a loss, which is indicated in the report in parentheses (-). Proper registration and reporting allows the company, although first the accountant of the enterprise should have a good understanding.
Formula for calculating profit before tax
The formula for calculating profit before tax looks quite cumbersome, so it is best to imagine the process of calculating the indicator in the form of several stages.
Calculation of gross profit or loss
Gross profit (loss) is the difference between the revenue the company received and the cost of products sold (or services provided).
It must be borne in mind that the cost of goods sold for trading and manufacturing enterprises is calculated differently. For example, employee wages can be classified as both direct and indirect costs. Typically, the company's accounting policy clearly defines how costs are calculated.
The formula for calculating gross profit is as follows:

Important: It is worth remembering that the result can be either positive (profit) or negative (loss).
Calculation of sales profit (or loss)
If we turn to the terminology used in the Income Statement, then sales profit is almost equivalent to operating profit and represents the difference between gross profit and operating expenses (selling and administrative).
Formula for calculating profit (loss from sales):

Important: when a company has received a gross loss, the calculated value of losses is inserted into the presented formula with a minus sign. We also must not forget that a negative result for calculating profit from sales is reflected in parentheses.
Calculation of profit before tax (or loss)
The final touch is to determine profit before tax directly as follows:

Important: as in the previous case, if the company received a loss from sales, then its amount is entered into the formula with a minus sign. When the result of calculating profit (loss) before tax becomes a negative value, this indicates an unprofitable and ill-considered economic activity of the organization. The loss in the accounting report is written in brackets.
Since the indicator in question is present in the Financial Results Report () - let’s present the formula in a different form, based on the line codes in the document:
Profit before tax (line 2300)= Profit (loss) from sales (line 2200) + Income from participation in other organizations (line 2310) + Interest receivable (line 2320) – Interest payable (line 2330) + Other income (line 2340) – Other expenses (2350 ).
The question often arises - what applies to other income and expenses? In fact, there is no definite answer, since each organization indicates these points in its accounting policies in accordance with existing legislation. For example, let's discuss. If a company owns land, it must pay tax. How to account for such an expense? You should focus on PBU 1/2008, which clearly states: the organization has the right to independently decide, based on its specifics and focus, where to allocate the amount of paid land tax. Some take it into account in other expenses, while others - in the costs of ordinary activities.
Important: when determining the income and expenses required for the formula, you should refer to the legislation - PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization” and PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”.
Example of calculating profit before tax
For clarity, let's look at an example - below is a fragment of the Financial Results Report:

The report shows the calculations made:
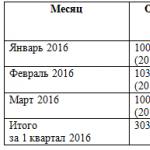
- Gross profit= 151033 – 142197 = 8836 thousand rubles.
- Revenue from sales= 8836 – 5826 – 1585 = 1425 thousand rubles.
- Profit before tax= 1425 +18 + 20 – 6 + 219 – 195 = 1481 thousand rubles.
Advice: if the profit does not please you, then you should do financial analysis - calculate turnover, liquidity, etc. This will allow you to draw conclusions about the state of affairs, on the basis of which you can develop a new strategy aimed at increasing sales and increasing profits.
Let's sum it up
Calculating profit before tax usually does not bring any particular difficulties to accountants if the accounting policy of the enterprise clearly defines what is included in the cost of products or services and which items are included in other income and expenses.
The discussed indicator allows you to subsequently calculate the amount of income tax, however, you must understand that tax and accounting are different, so there are situations when you cannot simply multiply the profit before tax by the tax rate to get the payment amount. In this case, you need to refer to PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax calculations”.
The purpose of doing business is to derive profit from the enterprise’s activities, both as stated in the organization’s charter and those that accompany its conduct. The amount of profit as a result of an enterprise’s activities can be assessed differently for tax, accounting and management purposes. One of the indicators that determines the size of the final profit of an economic entity is balance sheet profit; the formula for calculating balance sheet profit is based on the accounting data of the enterprise.
What does the balance sheet profit indicator reflect?
Balance sheet profit is understood as profit (loss) received before taxation for a certain period of time from all types of economic activities of an organization and reflected in its accounting records.
A company's balance sheet profit is an important analytical indicator that is used to evaluate the financial and economic activities of an enterprise, characterizing the amount of accountingly reliable profit, and in the case of its analysis for several reporting periods or business cycles, the dynamics of growth or decline in the overall efficiency of the company as a business entity.
Analysis of the basic and chain indices of the amount of balance sheet profit excludes the influence on the conclusions obtained on the basis of calculations, the size and dynamics of taxes payable (which will happen when comparing the size of net profit), which is important for management and planning.
Calculation of the “balance sheet profit” indicator
Balance sheet profit for the period characterizes as such the final financial result from all activities of the organization that had a monetary value. For balance sheet profit, the formula for calculating the indicator for the period is as follows:
Thus, book profit is the company's net income after paying all production, administrative and selling expenses for the period under review.
A positive difference means that the organization has a profit, a negative difference means a balance sheet loss for the period under review.
The “balance sheet profit” indicator itself is the basis for calculating the “net profit” indicator:
Reflection of balance sheet profit in accounting
The term “balance sheet profit” itself means that the value for it can be calculated by calculation from the accounting registers.
In balance sheet account 99 “Profits and Losses”, the balance accumulates during the year from the receipt of gross profit and profit from other operations from accounts 90 “Sales” and 91 “Other income and expenses” or losses on them. The balance sheet profit (or loss) of the enterprise for the period is equal to the turnover on account 99 in correspondence with the indicated accounts.
Account turnover is not included in the calculation of the indicator:
- reflecting in correspondence with account 68 the amounts of income tax to be paid;
- final turnover for the final assignment of net profit to account 84 for accounting for retained profit/loss.
Reflection of balance sheet profit in statutory reporting
If the term “balance sheet profit” itself is present, there is no line in the balance sheet with this name, which has its own justification and logic.
The organization's balance sheet presents aggregated indicators of the organization's assets and liabilities as of a specific reporting date according to the accounting registers. An organization's balance sheet profit is an indicator that accumulates on an accrual basis throughout the year, but is completely exhausted at the reporting date, being, according to accounting rules, allocated to accounts for taxes payable and accounts for net (retained) profit.
Consequently, on the reporting date in the balance sheet of the enterprise in an expanded sense (if we present it as a list of all accounts indicating the balances on them), the balance sheet profit will already be distributed and equal to zero, as will be the zero line with the same name in the balance sheet as a reporting form, if that was used.
Book profit is profit before tax. It is one of the key indicators when assessing business performance. Its value is used to determine the basis for calculating tax liabilities.
Balance sheet profit is...
The level of profitability has a direct impact on the amount of tax liabilities of the organization. The concept of “balance sheet profit of an enterprise” contains the summed up income from the main production processes. The value can be positive or negative. In the latter case, we will be talking about unprofitable activities.
The balance sheet profit of an enterprise is determined as the taxable base. If an error (even an insignificant one) is made in the process of deriving its final result, then for an economic entity this means an increased risk of a dispute with the fiscal authorities. Based on the results of an audit by the tax inspectorate, organizations will be fined for unreliable information and underpayment (overpayment) of tax.
Balance sheet profit can be obtained if expenses incurred are subtracted from the total volume of proceeds in monetary terms. Accrued taxes are not included in the cost group. The company's balance sheet profit includes:
- profit received from the sale of the company's main product (goods or services);
- financial result, determined after completion of operations on the sale of property, provision of it for temporary use to third parties on a paid basis;
- results of non-operating actions (from currency conversions, income from investment projects).
Balance sheet profit consists of profit from sales of main products with the share of this indicator at 80%. When calculating the profit value, accounting accounts and are used. The result of accumulation of funds on them and write-off at the end of the year is reflected in account 99. Turnover on account 99 should be equal to the level of book profit for the same period of time.
The concept of “balance sheet profit of an enterprise” includes various types of income, reduced by expenses incurred in the course of the company’s activities. Turnovers and balances on the following accounts are not taken into account:
- , showing the volume of tax liabilities;
- in terms of the final revolutions on it.
Balance sheet profit: calculation formula
You can derive the values of the balance sheet indicator of profitability of activities using data from balance sheets or information from financial statements. The balance sheet profit formula takes into account the following elements:
- Profit, the result of which is received after the sale of goods (Pr t).
- Profit generated as a result of the sale of property owned by the enterprise (Property).
- Profit that was generated from funds from non-operating income (Pr non-real).
How is book profit calculated:
Pr t + Pr im + Pr unreal
Pr t is defined as the difference between gross income from sales operations and production costs. It is calculated by reducing the proceeds from the sale of assets by their residual value and expenses that were incurred by the organization in the process of carrying out the transaction for the sale and delivery of the object to the buyer.
Balance sheet profit - a formula based on the balance sheet or account turnover allows you to calculate the percentage indicator of profitability of the costs incurred. To do this, you need to divide the derived numerical value of profit by the amount of expenses for the product groups sold. The last step is to convert the coefficient into percentages.
Balance sheet profit includes the following indicators from the Form 2 report:
- revenue indicated by line 2110;
- generated actual cost in full, taking into account management and commercial expense transactions;
- amounts of other income;
- amount of other costs.
There is no formula for balance lines. According to the financial statements, it can be derived on the basis of the statement of financial results (Form 2) according to the following scheme:
- line 2110 – (sum of lines 2120, 2210, 2220) + line 2340 – line 2350.
Balance sheet profit of the enterprise in reporting
Accounting statements reflect all performance indicators of companies. It allows you to assess the degree of success of a business project, calculate its profitability and prospects. The line in the balance sheet for book profit is not highlighted. The report shows the value of the profit remaining after deducting from it all types of costs and tax liabilities.
The reason for the impossibility of identifying the value of balance sheet profit according to the balance sheet reporting form is the different approach to reflecting the results of operations. The balance sheet is compiled on the basis of the ending account balances. Balance sheet profit must be calculated based on information generated cumulatively. The calculation can be made based on the balance and data from accounting registers. To do this, the amount of income tax paid during the year must be added to the retained earnings from the balance sheet line under code 1370.
Balance sheet profit is a line in Form 2, corresponding to the code designation 2300. If the company has a loss instead of a profit, then in the column with code 2300 its value is indicated without a minus, but the number is taken in parentheses.
Balance sheet profit is a value that shows how successfully a company has operated. If the result in the calculation formula is a positive number, then the organization has a profit. If the value is negative, there is a loss.
Balance sheet profit is a key reporting indicator
Balance sheet profit is the amount of profit an enterprise received during the period of operation from its main and non-core activities. The indicator is reflected in the balance sheet.
The concept of “balance sheet profit of an enterprise” contains the results of production, activity of an enterprise, a company for a period. This is the main financial indicator that shows the profit or loss received by the organization.
Balance sheet profit in reporting (form 2)
There are several types of profit on the income statement.
The following indicators exist:
- gross profit;
- profit (loss) from sales;
- profit (loss) before tax;
- Net income (loss).
As you can see, the concept of balance sheet profit is absent in the reporting (Form 2). The fact is that the balance sheet profit of an enterprise is a value that is considered a cumulative total from the beginning of the year. But it is not in the annual reports. The reason is the entries that the accountant makes at the end of the year and which reset certain accounting accounts. Therefore, we can say that the balance sheet profit of an enterprise is reflected in the reporting for the quarter, half a year and 9 months.
Formula for calculating gross profit:
Gross profit (line 2100) = Revenue (line 2110) - Cost (line 2120)
Line 2110 is a line in Form 2, which indicates revenue from the sale of products, goods, works, services. It is taken without value added tax and excise taxes.
Line 2120 shows the cost. That is, it includes expenses for ordinary activities.
To determine profit or loss from sales, calculate using the formula:
Profit (loss) from sales (line 2200) = Gross profit (line 2100) - Selling expenses (line 2210) - Administrative expenses (line 2220)
Balance line 2210- this is the amount of expenses from the normal activities of the organization. That is, this element of the formula is associated with the sale of goods, works, and services.
Line 2220 is all the costs that the company had and that are associated with managing the organization.
The calculation for profit before tax is as follows:
Profit (loss) before tax (line 2300) = profit (loss) from sales (line 2200) + Income from participation in other organizations (line 2310) + Interest receivable (line 2320) - Interest payable (line 2330) + Other income (line 2340) - Other expenses (line 2350)
To do this calculation, you must first complete lines 2310-2350 on your balance sheet income statement. Then we add the income to the figure of 2200, which was calculated earlier. Then we take into account expenses and get profit or loss. We look at the results in line 2300.
The formula for calculating balance sheet profit is as follows:
Balance sheet profit = line 2110 - line 2120 - line 2210 - line 2220 + line 2310 + line 2320 - line 2330 + line 2340 - line 2350
In annual reporting, balance sheet profit can be calculated as the sum of retained earnings from line 1370 and income taxes that the company must pay for the year.
Balance sheet profit in accounting
Balance sheet profit in accounting can be obtained using accounting accounts. Profit or loss from the activities of an organization is obtained as a result of the accumulation of a certain amount during the year on the balance sheet account 99 “Profit and Loss”. These values are also reflected in accounts 91 “Other income and expenses” and 90 “Sales”.
It turns out that the balance sheet profit or loss consists of the turnover of account 99 in correspondence with accounts 90 and 91.
When calculating book profit, do not take into account the amount of income tax payable (the current tax is line 2410 in Form 2). Taxes are reflected in account 68. Also, do not take into account the final closing of account 84, which turns the accumulated profit or loss of the current year into profit or loss of previous years.
How to calculate book profit: calculation formula
BP = Dod+ PD-Rod-PR
Basic elements of calculation:
- income from main activities (DoD);
- other income (PD);
- expenses from core activities (Gender);
- other expenses (PR).
If the calculation results result in a positive value, then the company made a profit for the period under review. A negative value indicates a loss.
If we subtract income tax (IP) from the resulting result, we obtain net profit (NP):
PE = BP-NP
Income includes:
- proceeds from sale;
- operating income;
- non-operating income.
However, the following is removed from income:
- amounts of taxes, such as VAT, excise taxes;
- sales tax and other taxes that apply to revenue;
- amounts that debtors transferred to you to repay loans and credits;
- prepayment amounts, advances;
- deposits and pledges;
- amounts collected under intermediary agreements to other individuals and companies.
Costs include:
- expenses for ordinary activities;
- operating expenses;
- non-operating costs.
Expenses do not include:
- acquisition and creation of fixed assets;
- acquisition of intangible assets and other non-current assets;
- contributions to the capital of other organizations;
- purchasing shares and other securities that are not intended to be resold in current transactions;
- transfers of funds under intermediary agreements;
- repayment of loans and borrowings;
- advance payment, advances issued, deposits towards payment.