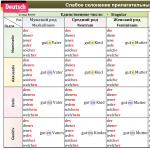
Regular and irregular verbs in English. Three verb forms in English. Main characteristics of regular verbs
Today's material will again be devoted to the great and powerful English verb. Why is the predicate in an English sentence given so much attention? Because it not only expresses any actions, but also indicates the time of their implementation. To be able to correctly convey the time of events, you need to know what regular verbs and irregular verbs are in English. This article will help you understand this important topic.
The British are very attentive to the delimitation of temporal moments, which is associated with a large number of different verb forms and combinations. Let us remember the system of these times.
There are four main aspects to the English language:
- Simple ( simple steps);
- Continuous ( ongoing processes);
- Perfect ( completed actions);
- Perfect Continuous ( actions are still in progress, but certain results have already been achieved).
And in each of these points, the Present, Past and Future tenses are distinguished accordingly.
The classification into regular and irregular verbs in English is associated with the formation of the past in and all types of tenses in. So let's get to the point.
In English grammar there is a general rule for constructing speech structures related to the past. According to this grammatical norm, every verb expressing past events must take the ending –ed. Moreover, this ending is the same for both the form in the Present Simple and for the past participle (Participle I), with the help of which constructions in the Perfect are formed.
| Infinitive | Transformation | Past tense |
| ask | +ed | asked |
| want | wanted | |
| visit | visited |
But sometimes it happens that the original use of words is firmly entrenched in speech and does not want to obey any newfangled rules. This is what happened with English verbs. Due to historical traditions, about 470 words are an exception to this rule. Accordingly, this is where the division into regular and irregular verbs of the English language comes from.
And if everything is clear about regular verbs, then the question arises, to what norm do irregular English verbs obey? But none. There is absolutely not a single rule that at least somehow generalizes the principles of changing them.
Some irregular verbs in the English language have forms that completely coincide with the infinitive. For others, everything seems to be written the same, but unexpectedly it reads differently. For others, 2 types of verb forms coincide, and for others, all three types have a different form.
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| put | put | put |
| read [read] | read [ed] | read [ed] |
| shoot | shot | shot |
| shake | shook | shaken |
To learn how to easily compose sentences with such verbs, there is no other way than to learn all forms by heart.
As we have already noted, the English language has approximately 470 irregular verbs. But we naturally do not call for teaching them all. It is enough to familiarize yourself with the most commonly used ones, of which, ironically, there are also many.
To facilitate understanding of this topic and further language learning, in the next section we will provide lists of popular English verbs of regular and irregular form. Skill comes with practice, so after a few lessons you will automatically use these words without thinking long about the rules and exceptions.
Popular regular verbs and irregular verbs in English
Let's look at 50 verbs of each type, most often used by the English in everyday speech.
Regular verbs
| Infinitive | Past simple = participle I | Translation |
| answer | answered | reply |
| ask | asked | ask, ask |
| believe | believed | trust, believe, believe |
| call | called | call, call |
| change | changed | replace, change |
| clean | cleaned | clean, tidy up |
| close | closed | close |
| cook | cooked | prepare |
| cry | cried | scream, cry |
| dance | danced | dance |
| decide | decided | decide |
| explain | explained | explain |
| finish | finished | complete, finish |
| hate | hated | hate |
| help | helped | to help |
| hope | hoped | hope |
| interest | interested | be interested |
| join | joined | connect, join |
| jump | jumped | jump |
| laugh | laughed | laugh |
| listen | listened | listen |
| live | lived | live |
| look | looked | take a look, look |
| love | loved | be in love |
| manage | managed | manage, cope |
| miss | missed | miss, miss |
| move | moved | move, move |
| need | needed | need |
| open | opened | open |
| paint | painted | to paint, to paint |
| pass | passed | pass, pass |
| play | played | play |
| prefer | preferred | prefer, serve |
| promise | promised | promise, assure |
| realize | realized | realize, understand |
| remember | remembered | remember, memorize |
| serve | served | serve, serve |
| start | started | start off |
| stop | stopped | stop |
| study | studied | study |
| talk | talked | talk, talk |
| touch | touched | touch |
| travel | travelled | travel |
| try | tried | try |
| use | used | use |
| walk | walked | go for a walk |
| want | wanted | want |
| wash | washed | wash, wash |
| watch | watched | look |
| work | worked | work |
Incorrect
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Participle I | Translation |
| be | was/were | been | to be, to exist |
| become | became | become | become, transform |
| begin | began | begun | begin, begin |
| bring | brought | brought | bring, deliver |
| build | built | built | build |
| buy | bought | bought | buy, purchase |
| catch | caught | caught | catch, catch |
| come | came | come | come, come |
| cost | cost | cost | cost |
| do | did | done | do, perform |
| draw | drew | drawn | paint |
| drink | drank | drunk | drink |
| drive | drove | driven | drive a car |
| eat | ate | eaten | eat |
| fall | fell | fallen | fall, fall |
| feel | felt | felt | feel |
| find | found | found | find |
| fly | flew | flown | fly, fly |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven | forgive |
| get | got | got | receive, get |
| give | gave | given | give |
| went | gone | go, head | |
| grow | grew | grown | grow, grow |
| have | had | had | have |
| hear | heard | heard | hear |
| keep | kept | kept | keep, store |
| know | knew | known | know |
| leave | left | left | leave, leave |
| let | let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain | lie |
| lose | lost | lost | lose, lose |
| make | made | made | do, produce |
| mean | meant | meant | mean, mean |
| meet | met | met | meet, meet |
| pay | paid | paid | to pay |
| read | read | read | read |
| run | ran | run | run |
| say | said | said | speak |
| see | saw | seen | see |
| send | sent | sent | send, send |
| show | showed | shown | show |
| sit | sat | sat | sit down, sit |
| sleep | slept | slept | sleep |
| speak | spoke | spoken | talk, talk |
| spend | spent | spent | spend, spend |
| take | took | taken | take, grab, take |
| tell | told | told | tell, talk, report |
| think | thought | thought | think |
| wake | woke up | woken | wake up |
| write | wrote | written | write |
Now you are familiar with the most frequently used regular verbs and popular irregular verbs in the English language. Each table contains the minimum that beginners need. We recommend that you print this material and use it as a cheat sheet for making various proposals. After several lessons, you won’t even notice how you remember most of the words by heart.
Irregular verbs in English - what are they? How do they differ from the correct ones? How can we know whether we are going to use a correct or irregular verb? How many irregular verbs do we need in everyday speech?
In most cases, to form the past tense, we add -ed to English verbs:
play - play ed, jump - jump ed, walk - walk ed, help - help ed(for details of writing and pronunciation of regular verbs in the past tense, see)
This is a rule, which means that such verbs are regular or regular. But there are also verbs in English that do not follow this rule - irregular, irregular. There are less than 3 percent of them, but they are the most common and most often used.
Irregular verbs are a legacy of the past.
Old English was even more complex; then verbs were also conjugated. Those verbs that are now regular were previously called “weak”, but there were seven more types of strong verbs. Many of the irregular English verbs are remnants of these seven types of strong verbs. Each of these seven groups has its own pattern for forming the past tense.
For example, teach, catch in the past tense become taught, caught
choose, freeze turn into chose, froze
Some verbs do not change at all: hit And quit remain hit And quit in the past time.
Over time, the English language has become simpler, many verbs have become regular. The researchers noticed an interesting pattern: the more often a word is used, the more likely it is to remain incorrect. It's easy to see that 10 most common English verbs irregular:
- I am - I was
- I have - I had
- Do you? — Did you?
These are all monosyllabic words of Anglo-Saxon origin. Besides them
- go (went), say (said), can (could), will (would), see (saw), take (took), get (got)
There is also a process of biological evolution of species in which changes in the most important genes propagate the least. But the evolution of language has some interesting features, for example, it occurs in different ways in different English-speaking countries:
dream, burn, learn
say the British.
dreamed, burned, learned Americans say
There are several such verbs that evolution, on the contrary, turned from regular to irregular, for example:
Sneaked
(sneaked) at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries it began to turn into Snuck,
and it hasn’t finished yet, but according to Harvard research, every year 1% of the English-speaking population “shifts” towards snuck
.
Lighted started to cut to lit not so long ago, both versions of this word are still acceptable.
Conclusion- you need to learn these irregular verbs. Or you learn them by heart ( by heart ), or on an intuitive level in the process of reading and listening to audio, they are acquired by themselves. It's nice to know that it has become much easier to learn irregular verbs now; in the past there were many more of them, and all people learning English, including native speakers themselves, had to learn them one way or another.
Irregular verbs in a table with audio
The most common irregular verbs in English
If you studied English as a child, then you are familiar with long tables with three forms of irregular verbs from school. But the regular verbs of the English language, despite their frequent use in speech, for some reason are always ignored and not studied in tabular form. And in vain, because they also have special grammatical cases. In addition, by memorizing a whole list of regular verbs, we will expand our vocabulary and feel more confident when constructing sentences, without a doubt putting any verb into the form required by the context. But first, let’s remember once again what rule gave the name to such verbs.
Forms of regular English verbs
As you remember, in English grammar there are only four verb forms. Two of them do not require close study: we become familiar with the infinitive when we work on learning new words, and the present participle (Participle I) is invariably formed by adding the ending –ing. There remain two forms, according to which the division into regular English verbs and irregular ones occurs.
According to the grammatical norm*, the formation of the Past Simple (simple past) and Participle II (past participle) occurs by adding the ending –ed to the stem of the word. Accordingly, the appearance of these verb forms is the same.
*Exceptions to this rule are precisely the class of irregular verbs.
But not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. Adding an ending has its own phonetic and grammatical nuances associated with linguistic features. The following grammar table will help you avoid incorrect formation and pronunciation of past tense forms.
| Grammar rules | |
| Rule | Example |
| For verbs ending in -e, the final vowel is not doubled, i.e. only the letter d is added. | ti e-tie d (tie)
lik e–like d (like) queu e–queue d (stand in line) |
| If a word has one syllable and it ends with a consonant, then it is doubled. | kni t–kni tted (to knit)
pla n– pla nned (to plan) ro b– ro bbed (rob) |
| The final l when adding an ending always requires duplication. | travel l– travel lled (travel) |
| Verbs ending " consonant+y", replace the last letter with i. | t ry-t Ried (try)
hur ry– hur Ried (hurry) car ry– car Ried (carry) |
| Words ending in –y with a preceding vowel add the ending –ed as standard. | enj oh– enj oyed (enjoy)
st ay– st ayed (stand) pray – pra yed (pray) |
| Pronunciation nuances | |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiced d if it is preceded by a voiced sound. | live-li ved (live)
phone - phon ed (call) |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiceless t if it is preceded by a voiceless sound. | swap – swap ped (exchange)
finish – finish shed (end) |
| The ending is pronounced as a voiced id if preceded by the letters d or t. | study – stu died (study)
wait-wai ted (wait) |
Now we are familiar with all the important points related to the correct formation of verb forms. It's time to get acquainted with the popular representatives of this class of verbs. The table below will present the most common regular verbs with translation and their pronunciation in English.
Regular English verbs – 50 words with transcription and translation
So, we bring to your attention the basic regular verbs in English with transcription and translation.
| Top 50 Regular English Verbs | |||
| Infinitive | Past Simple=
Past Participle |
Transcription | Translation |
| agree | agreed | [əˈɡriː – əˈɡriːd] | agree |
| allow | allowed | [əˈlaʊ – əˈlaʊd] | allow |
| answer | answered | [‘ɑːnsə - ɑːnsəd] | reply |
| arrive | arrived | [əˈraɪv – əˈraɪvd] | arrive |
| believe | believed | believe | |
| call | called | call, call | |
| close | closed | close | |
| cook | cooked | prepare | |
| copy | copied | [ˈkɒpi – ˈkɒpid] | copy |
| cry | cried | scream, cry | |
| decide | decided | decide | |
| defend | defended | protect | |
| discuss | discussed | discuss | |
| dry | dried | dry | |
| explain | explained | [ɪkˈspleɪn – ɪkˈspleɪnd] | explain |
| happen | happened | [ˈhæpən — ˈhæpənd] | happen, occur |
| help | helped | to help | |
| invite | invited | [ɪnˈvaɪt - ɪnˈvaɪtɪd] | invite |
| jump | jumped | jump | |
| listen | listened | [ˈlɪsn – ˈlɪsnd] | listen |
| look | looked | look | |
| love | loved | be in love | |
| manage | managed | manage, cope | |
| marry | married | marry | |
| move | moved | move, move around | |
| need | needed | need | |
| offer | offered | [ˈɒfə – ˈɒfəd] | suggest |
| open | opened | [ˈəʊpən — ˈəʊpənd] | open |
| play | played | play | |
| prefer | preferred | prefer | |
| prepare | prepared | ready | |
| promise | promised | promise | |
| reach | reached | achieve | |
| realize | realized | [ˈriːəlaɪz - ˈriːəlaɪzd] | understand, realize |
| remember | remembered | remember, recall | |
| return | returned | come back | |
| save | saved | keep | |
| smile | smiled | smile | |
| start | started | start off | |
| stop | stopped | stop | |
| surprise | surprised | surprise | |
| switch | switched | switch | |
| talk | talked | talk, chat | |
| thank you | thanked | [θæŋk - θæŋkt] | thank |
| translate | translated | transfer | |
| use | used | to use, to use | |
| want | wanted | want, desire | |
| watch | watched | look | |
| work | worked | work | |
| worry | worried | [ˈwʌri – ˈwʌrɪd] | worry, worry |
Congratulations, we have studied over 50 words if we take into account the example verbs used in the theoretical part. Now you not only know what regular English verbs are in theory, but you can also give many practical examples of them. Be sure to continue to improve your English and see you in new classes!
Views: 398
English is a language of exceptions, where when learning a new grammatical rule, students are faced with a dozen buts in which this rule does not apply. One of these rules is the use of irregular verbs in the past tense. For many English learners, this topic is a nightmare. But you can’t do without them, because these are the realities of English! However, there is good news - modern English is gradually getting rid of irregular verbs, replacing them with regular ones. Why and how - we'll look at it in the article.
Why are English verbs irregular?
Not only foreigners, but also native speakers themselves experience difficulty in using irregular verbs. But nevertheless, for English philologists, the non-standardity of this part of speech is not a drawback, but a reason for pride. They believe that irregular verbs are a cultural monument that perpetuates the history of the English language. The explanation for this fact is the Germanic roots of the origin of irregular verbs, which makes British English a traditional variant of the language. For comparison, Americans are trying hard to get rid of the irregular shape, converting it into the correct one. Therefore, the list of non-standard verbs increases for those who learn both versions of the language. Thus, the incorrect version is ancient, which is reflected in prose and poetry.
How many forms does a verb have in English?
Speaking about verbs in English, it should be noted that they have 3 forms:
- infinitive, aka ;
- I, or Participle I, - this form is used in the simple past tense (Past Simple) and the 2nd and 3rd cases of the conditional mood (Conditional of the 2-d and of the 3-d case);
- Past Participle II, or Participle II, for the simple perfect tense of the past tense (Past Perfect), passive voice (Passive Voice) and conditional of the 3-d case.

The table "Three in English" is presented later in the article.
What are regular and irregular verbs? Education rules
Regular verbs are those in which the past form (Past Simple) and the form Participle II (Participle II) are formed by adding the ending -ed to the initial form. The table "Three verb forms in English. Regular verbs" will help you better understand this rule.
There are some features when forming Participle I and Participle II:
- if the verb ends with the letter -e, then adding -ed does not double it;
- The consonant in monosyllabic verbs is duplicated when added. Example: stop - stopped (stop - stopped);
- if the verb ends in -y with a preceding consonant, then y changes to i before adding -ed.
Verbs that do not obey the general rule in the formation of tense forms are called irregular. In English, these include the Past Simple and Participle II verb forms.
Irregular verbs are formed using:
ablauta, in which the root changes. Example: swim - swam - swum (swim - swam - swam);
the use of suffixes different from those accepted in the grammar of the language. Example: do - did - done (do - did - did);
identical or unchangeable form. Example: cut - cut - cut (cut - cut - cut).
Due to the fact that each irregular verb has its own inflection, they should be learned by heart.
There are a total of 218 irregular verbs in the English language, of which approximately 195 are in active use.
Recent research in the field of language shows that rare verbs are gradually disappearing from the language due to the replacement of the 2nd and 3rd forms with forms of the regular verb, that is, the addition of the ending - ed. This fact is confirmed by the table “Three verb forms in English” - the table presents a number of verbs that have both regular and irregular forms.
table of irregular verbs
The table "Three Forms of Irregular Verbs in English" includes the most frequently used verbs. The table shows 3 forms and translation.

Irregular verbs came to modern English from Old English, which was spoken by the Angles and Saxons - British tribes.

Irregular verbs evolved from so-called strong verbs, each of which had its own type of conjugation.

Researchers from Harvard found that the majority of verbs used are irregular, and they will remain so because they are used more often than others.

There is also a phenomenon in the history of the English language when a regular verb became irregular. For example, sneak, which has 2 forms - sneaked and snuck.

Not only English learners have problems with verbs, but also native speakers, as even they find themselves in awkward situations when it comes to this difficult part of speech.

One of them is Jennifer Garner, who all her life was sure that sneak was the correct verb.

She was corrected by the host of one of the programs in which the actress took part. With a dictionary in hand, he pointed out to Jennifer her mistake.

Therefore, you should not be upset if you make mistakes when using irregular verbs. The main thing is that they do not become systematic.

Regular verbs
The table "Three forms of regular verbs in English with transcription and translation" is compiled on the basis of the most frequently used verbs.
Past Participle I and II |
|||
ask | |||
answer | |||
allow | |||
agree | |||
borrow, borrow | |||
copy, rewrite | |||
prepare | |||
close | |||
carry, drag | |||
call, call | |||
discuss | |||
decide, decide | |||
explain | explain | ||
slide | |||
cry, scream | |||
finish, finish, end | |||
shine | |||
rub | |||
grab | |||
to help | |||
happen, happen | |||
manage | |||
look | |||
like | |||
move, move | |||
manage | |||
to be necessary, to need | |||
open | |||
recall | |||
suggest | sadgesture | ||
study, learn | |||
stop, cease | |||
start off | |||
travel | |||
speak | |||
transfer | translate | ||
try, try | |||
use | |||
worry | |||
walk, walk | |||
look | |||
work |
Examples of using 3 forms of verbs with translation
Above we looked at 3 forms of verbs in English. A table with examples of use and translation will help reinforce the topic.

Here, for each grammatical construction, two examples are given - one with regular and one with irregular verbs.
Grammar design | Example in English | Translation |
| Past Simple |
|
|
| Present Perfect Tense |
|
|
| Past Perfect Tense |
|
|
| Passive Voice |
|
|
| Conditional |
|
|
Exercises

To better memorize irregular verbs, you need not only to learn them by heart and repeat them, but also to perform various exercises.
Exercise 1. Here is the table "Three verb forms in English. Irregular verbs." Fill in one of the three missing forms.
Exercise 2. Here is the table "Three verb forms in English. Regular verbs." Insert forms Participle I and II.
Exercise 3. Using the tables, translate the following sentences into English.
- I was reading a book.
- We saw them yesterday.
- The Smiths lived in London until 2000. They then moved to Manchester.
- Alice was a university student in 2014.
- They worked in the same company two years ago.
- He just finished training.
- When we were children, my mother often took us to this park.
- I drove a toy car as a child.

Answers to exercises
Exercise 1.
Exercise 2.
asked, borrowed, closed, decided, explained, helped, started, traveled, used, worked.
Exercise 3.
- I read a book.
- We saw them yesterday.
- The Smiths lived in London till 2000. Then they moved to Manchester.
- Alice was a student of Univercity in 2014.
- They worked in the same company two years ago.
- He has just finished training.
- When we were children we took for a walk to this park.
- I drove a toy car in my childhood.
Make it a habit to periodically repeat the basic forms of the English verb. A table with irregular verbs, doing exercises and periodic repetition will help you quickly cope with the difficulties of the English language.
Most grammar reference books pay little attention to the topic of regular English verbs. In fact, these words have their own characteristics that all students need to become familiar with.
Main characteristics of regular verbs
This group of words is distinguished by the way they form the past tense. Regular verbs add the ending -ed to the stem. The remaining cases are considered exceptions, calling those words incorrect. When attaching an ending to a stem, it is important to remember some cases of its interaction with final consonants and vowels:
- if the verb ends in -e, it is removed: manage – managed (to cope, to succeed);
- the final consonant is doubled if it is preceded by a short stressed vowel: knit – knitted (knit);
- if there is a consonant before the final -y, this letter is replaced by -i: study – studied (to study, study);
- When the letter -y at the end of a verb is preceded by another vowel, -y remains: play – played (play).
The rules for adding the ending -ed are necessary to prevent errors in writing. But the pronunciation of such verbs also varies depending on the final sound of the stem:
- the ending -ed is read as [d] if it is preceded by a vowel or a voiced consonant: allow – allowed [əˈlaʊd] (to allow), stay – remained (to remain), worry – worried [ˈwʌrid] (to worry);
- -ed conveys the sound [t] after voiceless consonants: work – worked (work), discuss – discussed (discuss);
- -ed is pronounced as when the verb ends in t or d: admit – admitted [əd’mɪtid] (to admit).
There are more regular verbs in English than irregular ones, but there is no need to remember them all. It is enough to learn the features of adding the ending of the past tense and its pronunciation.
Table of regular verbs in English
For informational purposes, students should pay attention to a small summary table of these words. It also covers the basic rules of regular verbs in English.
| Initial form | Transcription | Past tense | Transcription | Translation |
| agree | [əˈɡriː] | agreed | [əˈɡriːd] | agree |
| allow | [əˈlaʊ] | allowed | [əˈlaʊd] | let |
| answer | [‘ɑːnsə] | answered | [‘ɑːnsəd] | reply |
| arrive | [əˈraɪv] | arrived | [əˈraɪvd] | arrive |
| believe | believed | believe | ||
| borrow | [ˈbɒrəʊ] | borrowed | [ˈbɒrəʊd] | occupy |
| call | called | call, call | ||
| change | changed | change | ||
| confess | confessed | to acknowledge | ||
| cook | cooked | prepare | ||
| cry | cried | cry, scream | ||
| decide | decided | decide | ||
| dry | dried | dry | ||
| explain | [ɪkˈspleɪn] | explained | [ɪkˈspleɪnd] | explain |
| express | [ɪksˈpres] | expressed | [ɪksˈprest] | to express |
| finish | [ˈfɪnɪʃ] | finished | [ˈfɪnɪʃt] | end |
| greet | greeted | to greet | ||
| handle | handled | address | ||
| help | helped | to help | ||
| invent | [ɪnˈvent] | invented | [ɪnˈventid] | invent |
| judge | [ʤʌʤ] | judged | [ʤʌʤd] | judge |
| knit | knitted | to knit | ||
| locate | located | settle down | ||
| love | loved | be in love | ||
| marry | married | marry | ||
| manage | managed | manage | ||
| neglect | neglected | neglect | ||
| offer | [ˈɒfə] | offered | [ˈɒfəd] | suggest |
| open | [ˈəʊpən] | opened | [ˈəʊpənd] | open |
| play | played | play | ||
| promise | promised | promise | ||
| return | returned | come back | ||
| stop | stopped | stop | ||
| talk | talked | speak | ||
| use | used | use | ||
| want | wanted | want |