The concept of the pH of the pH school level. Hydrogen indicator of acidity (pH). pH in arterial and venous blood, plasma and serum
The level of activity of hydrogen ions in water is one of the most important factors affecting the assessment of fluid quality. The level of acid-base balance and the direction of biochemical reactions that will occur in the body after drinking this liquid depend on this criterion. In this article we will dwell on the question of what is pH of water, how is it determined, and also how to increase or decrease pH of water.
From this article you will learn:
What is pH of water
What is the norm of pH of water
What threatens the low pH of water
How to measure pH of water
What is pH of water
The pH is a unit of activity of the hydrogen ion, which is equal to the inverse logarithm of the activity of hydrogen ions. So, for example, water, whose pH is 7, has 10–7 mol per liter of hydrogen ions. Consequently, a liquid with a pH of 6–10–6 mol per liter. The pH scale in this case ranges from 0 to 14. If the pH of the water is less than 7, then it is acidic, and if more than 7 - then alkaline. The pH for surface water systems is 6.5–8.5, for underground - 6–8.5.
The pH of water is 7 at 25 ° C, but when interacting with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, this value will be 5.2. The pH level is closely related to atmospheric gas and temperature, so water should be checked as soon as possible. The pH of the water will not be able to give a complete description and reason to limit the flow of water.
When various chemicals are dissolved in water, this balance is subject to change, which in turn provokes a change in pH. If acid is added to water, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, and the concentration of hydroxide ions, in turn, decreases. If alkali is added to the liquid, then the concentration of hydroxide ions increases, and the content of hydrogen ions decreases.
The pH level of water indicates the level of acidity or alkalinity of the medium, and acidity and alkalinity are characterized by the quantitative content of elements in the water that neutralize alkali and acid. So, for example, temperature reflects the level of heating of a substance, but not a quantitative indicator of heat. If we touch the water with our hand, we will determine whether it is warm or cold, but we cannot say how much heat is contained in it (in other words, how long it takes for the water to cool).
PH is one of the main quality characteristics of water. It reflects the acid-base balance and determines how certain biological and chemical processes will occur. The pH value of water determines the rate of a particular chemical reaction, the level of corrosiveness of a liquid, the degree of toxicity of a pollutant, and many other factors. Moreover, the acid-base balance of the body environment determines our state of health, mood and well-being.
The following groups of water are distinguished, depending on the pH value:
It is necessary to control the pH level of water at each stage of liquid purification, since a balance shift can negatively affect the taste, smell and shade of the water, as well as reduce the efficiency of its purification.
What is the normal pH of water
Due to the rapid pace of modern life, malnutrition, violation of food and drinking regimes, the pH level in the human body drops. So, the acid-base balance shifts towards increased acidity (pH to 7 means an acidic environment, and up to 14 - alkaline, respectively, the lower this level, the higher the acidity), which can lead to serious diseases. This problem can be solved by daily consumption of mineral water with an optimal level of activity of hydrogen ions. That is why it is important to know what pH value is the norm for the water that you regularly eat.

So, what should be the pH of water? Professionals argue that this value should roughly correspond to the normal pH value of human blood (7.5). That is why for drinking water, the pH rate is calculated from 7 to 7.5. Thanks to clean drinking water with a normal indicator of the activity of hydrogen ions, metabolic processes in the body improve, the total life span increases, and oxygen metabolism is optimized. Conversely, due to the sweet, carbonated and dye-containing drinks, the pH of human blood decreases, which can be immediately noticed by the unpleasant dry mouth.
Therefore, it is best to give preference to water with the “correct” pH value. You can always find this information on the label of any bottle. No filter with fillers and absorbents can replace real natural water with an optimal pH level. Some people try to lower the acidity of water pH and give the liquid useful properties by adding lemon or cucumber juice, however, this does not always have the desired effect. Another well-known method for changing the pH of water is electrolysis, which allows you to get alkaline and acidic water in two containers. Alkaline water with high pH is considered “live”, it is used for treatment, and acidic water is “dead”, which is most often used for washing.
However, such methods are not suitable for daily use. In this situation, there is only one rational decision - to give preference to low-mineral natural water with the necessary level of acidity for health.
PH measurement of water
Do not forget that the human body consists of water for as much as 70%! Metabolic products in the cells are acids, while the bulk of the body’s internal fluids, with the exception of stomach acid, are slightly alkaline. Of particular importance are blood counts. The human body functions normally if its blood is weakly alkaline, and its pH value is from 7.35 to 7.45.
In the case when a large amount of acids gets into the blood and intercellular fluid, acid-base balance is disturbed. Even a slight deviation of the pH level from these indicators (from 7.35 to 7.45) can lead to serious health problems. If the process of increasing blood acidity and a further decrease in pH to 6.95 continues, then there is a coma and there is a real risk to human life! For this reason, it is necessary to monitor the pH value of drinking water, which is one of the most important indicators of its quality!
- Litmus paper.
You can determine the pH level of water yourself, at home. As a device for measuring pH of water, you can use litmus (indicator) paper, which changes its color when briefly immersed in the studied medium. So, when immersed in an acidic medium, the litmus strip acquires a red tint, and in an alkaline one it turns blue. Next, you should compare the resulting color with a color scale, in which for each shade there corresponds a specific pH level in order to determine this indicator for the studied fluid. This method of determining pH is the simplest and cheapest.
- PH meter.
For the most accurate determination of the pH level, a pH meter for water is used. This device for determining pH of water is more expensive than litmus paper, nevertheless it determines the level of pH of liquid to the nearest hundredth!
PH meters for water are domestic (portable) and laboratory. Most often they use the first option, we will dwell on them in more detail. They differ:
Degree of protection against water.
The presence (or absence) of automatic calibration.
The accuracy of the results.
The last parameter is determined by the number of calibrated points (1 or 2). Points are called buffer solutions, with the help of which the pH meter is calibrated. We recommend purchasing an instrument with automatic calibration.
- Homemade test strips.
There are special test strips that determine the level of pH environment. Such strips are very convenient to use. Their packaging is equipped with a scale by which the concentration of hydrogen ions is determined. But such test strips do not appear on sale so often, and they are quite expensive.
With all its advantages, pH meters for water also have a relatively high price.
You can use homemade test strips to determine the pH of the water.
There are various substances that change color depending on the content of hydrogen ions in a liquid. For example, instead of a brown shade, tea becomes yellow if a slice of lemon is added to it.
In the same way, their color changes, depending on the content of hydrogen ions, cherry, currant juices, etc. In nature, there are a huge number of such organic indicators. And on the basis of such indicators create home-made test strips that allow you to determine the pH of water.
We will use the substance that is part of red cauliflower. This vegetable contains anthocyanin pigment, which belongs to the category of flavonoids. It is he who is responsible for the shade of cabbage juice and changes it, depending on the level of acidity.
Anthocyanins acquire a red tint in an acidic environment, and a blue tint in an alkaline environment, and they turn purple in a neutral environment. Beet pigment has similar properties.
For the experiment, you need half a boil of medium-sized red cauliflower, which should be finely chopped. Then chopped cabbage must be put in a container and pour a liter of water. Then boil water and leave this potion to boil for 20-30 minutes.
During this time, part of the liquid will evaporate, and you will get a broth of a saturated purple hue. Then cool the potion and prepare the basis for the test.
An ideal option in this case is white printer paper, which will not introduce errors in the color of the liquid. Also, its advantage is that it absorbs the decoction of the indicator well. The paper should be cut into strips of approximately 1 × 5 cm.
Before you determine the pH level of water, it is necessary to soak the test strips with an indicator solution. To do this, strain the cooled broth through cheesecloth and lower the paper into it. Ensure that the test strips are saturated evenly. Impregnate paper for 10 minutes. As a result, the paper should acquire a pale lilac hue.
When the paper, saturated with the decoction, has dried, you can begin to determine the pH level of water. Then fold the test strips into a box or plastic bag to protect them from moisture.
Using this method of determining the level of pH is very easy. Take a dropper and drip one or two drops of the test solution onto the test strip. Wait one to two minutes for the indicator to react with the paper. Depending on the pH value of water, the paper will acquire a certain shade, which should be compared with a color scale, which has the following form:
 To calibrate the color scale, substances are used that in their original form have a constant pH of the medium. Below is a detailed table of these elements:
To calibrate the color scale, substances are used that in their original form have a constant pH of the medium. Below is a detailed table of these elements: This table will help you if you want to conduct an experiment using some other indicator (for example, beetroot broth, blackcurrant juice or mulberry).
If the result obtained does not inspire confidence, or for some reason you could not solve the problem of unbalanced pH of water, then contact the professionals.
There are many companies in the Russian market that are involved in the development of water treatment systems. It is quite difficult to choose one or another type of filter for water purification independently, without the help of a professional. And even more so, you should not try to mount a water treatment system yourself, even if you read several articles on the Internet and it seems to you that you figured it out.
our company Biokit It offers a wide selection of reverse osmosis systems, water filters and other equipment that can return its natural characteristics to tap water.
The specialists of our company are ready to help you:
connect the filtration system yourself;
to understand the process of choosing filters for water;
pick up replacement materials;
fix problems or solve problems with the help of installers;
find answers to your questions by telephone.
Entrust Biokit systems to water purification - let your family be healthy!
PH and its effect on the quality of drinking water.
What is pH?
pH ("Potentia hydrogeni" is the strength of hydrogen, or "pondus hydrogenii" is the weight of hydrogen) is a unit of measurement of the activity of hydrogen ions in any substance, quantitatively expressing its acidity.
This term appeared at the beginning of the twentieth century in Denmark. The pH was introduced by the Danish chemist Soren Peter Lauritz Sorensen (1868-1939), although claims about a certain “power of water” are also found in his predecessors.
Hydrogen activity is defined as the negative decimal logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions, expressed in moles per liter:
pH \u003d -log
For simplicity and convenience, a pH value was introduced in the calculations. The pH is determined by the quantitative ratio in water of H + and OH- ions formed during dissociation of water. It is customary to measure pH on a 14-digit scale.
If the water has a reduced content of free hydrogen ions (pH greater than 7) compared with hydroxide ions [OH-], then the water will have alkaline reaction, and with a high content of H + ions (pH less than 7) - acid reaction. In perfectly pure distilled water, these ions will balance each other.
acidic environment:\u003e
neutral environment: \u003d
alkaline environment:\u003e
When the concentrations of both types of ions in a solution are the same, they say that the solution has a neutral reaction. In neutral water, the pH is 7.
When various chemicals are dissolved in water, this balance changes, which leads to a change in the pH value. When acid is added to water, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, and the concentration of hydroxide ions decreases accordingly, when alkali is added, on the contrary, the content of hydroxide ions increases, and the concentration of hydrogen ions decreases.
pH reflects the degree of acidity or alkalinity of the medium, while “acidity” and “alkalinity” characterize the quantitative content of substances in water that can neutralize alkali and acid, respectively. As an analogy, we can give an example with a temperature that characterizes the degree of heating of a substance, but not the amount of heat. Dipping our hand in the water, we can say which water is cool or warm, but we can’t determine how much heat is in it (i.e., relatively speaking, how long this water will cool).
pH is considered one of the most important indicators of the quality of drinking water. It shows acid-base balance and affects how the chemical and biological processes proceed. Depending on the pH, the rate of chemical reactions, the degree of corrosiveness of water, the toxicity of pollutants, etc., can vary. Our well-being, mood and health directly depend on the acid-base balance of our body’s environment.
Modern man lives in a polluted environment. Many acquire and consume food made from convenience foods. In addition, almost every person is exposed to stress daily. All this affects the acid-base balance of the body environment, displacing it in the direction of acids. Tea, coffee, beer, carbonated drinks reduce the pH in the body.
It is believed that an acidic environment is one of the main causes of cell destruction and tissue damage, the development of diseases and aging processes, the growth of pathogens. In an acidic environment, building material does not reach the cells, the membrane is destroyed.
Outwardly, the state of acid-base balance of human blood can be judged by the color of its conjunctiva in the corners of the eyes. With an optimal acid-base balance, the conjunctiva color is bright pink, but if a person increases blood alkalinity, the conjunctiva acquires a dark pink color, and with an increase in acidity, the conjunctiva color becomes pale pink. Moreover, the color of the conjunctiva changes already 80 seconds after the use of substances that affect the acid-base balance.
The body regulates the pH of internal fluids, maintaining values \u200b\u200bat a certain level. The acid-base balance of the body is a certain ratio of acids and alkalis, contributing to its normal functioning. The acid-base balance depends on maintaining relatively constant proportions between the intercellular and intracellular waters in the tissues of the body. If the acid-base balance of fluids in the body is not constantly maintained, normal functioning and maintenance of life will be impossible. Therefore, it is important to control what you consume.

Acid-base balance is our indicator of health. The more acidic we are, the sooner we get older and more ill. For the normal functioning of all internal organs, the pH level in the body must be alkaline, in the range from 7 to 9.
the pH inside our body is not always the same - some of its parts are more alkaline and some are acidic. The body regulates and maintains homeostasis of the pH level only in individual cases, such as blood pH. The pH of the kidneys and other organs whose acid-base balance is not regulated by the body is affected by the food and drinks that we consume.
blood pH
The pH level of the blood is maintained by the body in the range of 7.35-7.45. 7.4-7.45 is considered a normal indicator of human blood pH. Even a slight deviation of this indicator affects the ability of the blood to carry oxygen. If the blood pH rises to 7.5, it carries 75% more oxygen. With a decrease in blood pH to 7.3, it is already difficult for a person to get out of bed. At 7.29 he can fall into a coma, if the pH of the blood drops below 7.1, the person dies.
Blood pH should be maintained in a healthy range, so the body uses organs and tissues to maintain its constancy. As a result, the pH level of the blood does not change due to the use of alkaline or acid water, but the tissues and organs of the body used to adjust the pH of the blood change their pH.
kidney pH
The pH of the kidneys is affected by water, food, metabolic processes in the body. Acidic foods (e.g. meat products, dairy products, etc.) and drinks (soft drinks, alcoholic drinks, coffee, etc.) lead to a low pH in the kidneys, because the body removes excess acidity through the urine. The lower the urine pH, the harder it is for the kidneys to work. Therefore, the acid load attributable to such foods and drinks on the kidneys is called the potential acid-kidney stress.
The use of alkaline water brings benefits to the kidneys - there is an increase in the pH level of urine, and the acid load on the body decreases. Increasing the pH of urine increases the pH of the body as a whole and relieves the kidney of acid toxins.
pH of the stomach
An empty stomach contains no more than a teaspoon of stomach acid produced in the last meal. The stomach produces acid as needed when eating food. The stomach does not secrete acid when a person drinks water.
It is very beneficial to drink water on an empty stomach. The pH increases in this case to the level of 5-6. An increased pH will have a mild antacid effect and will lead to an increase in the number of beneficial probiotics (beneficial bacteria). Increasing the pH of the stomach increases the pH of the body, which leads to healthy digestion and relieves symptoms of indigestion.
subcutaneous fat pH
The body’s adipose tissue has an acidic pH because excess acid is deposited in it. The body has to store acid in adipose tissues when it cannot be excreted or neutralized in other ways. Therefore, the shift in the pH of the body to the acidic side is one of the factors of excess weight.
The positive effect of alkaline water on body weight is that alkaline water helps to remove excess acid from tissues, as it helps the kidneys work more efficiently. This helps to control weight, because the amount of acid that the body must "store" is repeatedly reduced. Alkaline water also improves the results of a healthy diet and exercise, helping the body cope with the excess acidity secreted by fatty tissue during weight loss.
Bones
Bones have an alkaline pH, as they are mainly composed of calcium. Their pH is constant, but if the blood needs a pH adjustment, calcium is taken from the bones.
The benefits of alkaline water to bones are to protect them by reducing the amount of acid that the body has to fight. Studies have shown that drinking alkaline water reduces bone resorption - osteoporosis.
liver pH
The liver has a slightly alkaline pH, the level of which is affected by both food and drinks. Sugar and alcohol must be broken down in the liver, and this leads to excess acid.
The benefits of alkaline liver water are the presence of antioxidants in such water; It was found that alkaline water enhances the work of two antioxidants located in the liver, contributing to a more effective purification of blood.
body pH and alkaline water
Alkaline water allows parts of the body that maintains the pH of the blood to work with greater productivity. Raising the pH level in the parts of the body responsible for maintaining the pH of the blood will help these organs stay healthy and work quickly.
Between meals, you can help your body normalize its pH by consuming alkaline water. Even a slight increase in pH can have a huge impact on your health.
According to research by Japanese scientists, the pH of drinking water, which is in the range of 7-8, increases the life expectancy of the population by 20-30%.
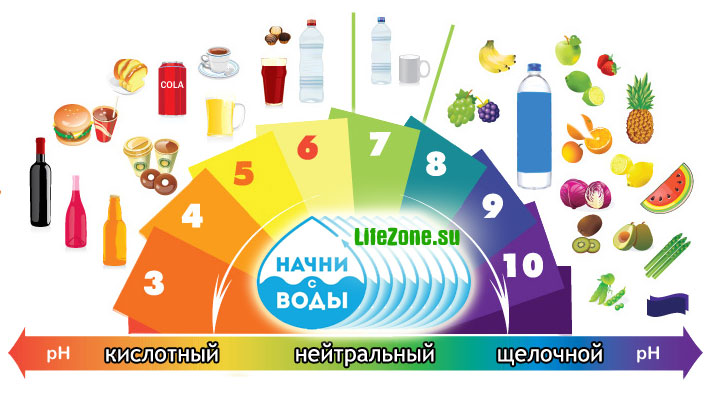
Depending on the pH level, water can be divided into several groups:
Strongly acidic waters< 3
acidic waters 3 - 5
slightly acidic waters 5 - 6.5
neutral waters 6.5 - 7.5
slightly alkaline waters 7.5 - 8.5
alkaline waters 8.5 - 9.5
highly alkaline waters\u003e 9.5
Typically, the pH of drinking tap water is within the range at which it does not directly affect consumer water quality. In river waters, the pH is usually in the range 6.5–8.5, in precipitation 4.6–6.1, in marshes 5.5–6.0, and in sea waters 7.9–8.3.
WHO does not offer any recommended medical value for pH. It is known that at low pH, water has high corrosivity, and at high levels (pH\u003e 11), water acquires a characteristic soapiness, an unpleasant odor, and can cause irritation to the eyes and skin. That is why for drinking and household water, the pH level in the range from 6 to 9 is considered optimal.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



Interesting to know: The German biochemist OTTO WARBURG, awarded in 1931 the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, proved that oxygen deficiency (acidic pH<7.0) в тканях приводит к изменению нормальных клеток в злокачественные.
The scientist discovered that cancer cells lose their ability to develop in an environment saturated with free oxygen with a pH value of 7.5 and higher! This means that when the fluids in the body become acidic, cancer is stimulated.
His followers in the 60s of the last century proved that any pathogenic flora loses its ability to reproduce at pH \u003d 7.5 and higher, and our immune system can easily cope with any aggressors!
To maintain and maintain health, we need the right alkaline water (pH \u003d 7.5 and higher). This will make it possible to better maintain the acid-base balance of body fluids, as the main living environments have a slightly alkaline reaction.
Already in a neutral biological environment, the body may have an amazing ability to heal itself.

Do not know where to get proper water ? I'll tell you!

Note:
Pressing the button " Discover»Does not lead to any financial expenses and obligations.
You only get information on the availability of the right water in your area.,
and get a unique opportunity to become a member of the Healthy People Club for free
and get a 20% discount on all offers + cumulative bonus.

Join the international health club Coral Club, get a FREE discount card, the opportunity to participate in promotions, an accumulative bonus and other privileges!

Acidity (lat. aciditas) is a characteristic of the activity of hydrogen ions in solutions and liquids.
In medicine, the acidity of biological fluids (blood, urine, gastric juice and others) is a diagnostically important parameter of the patient’s health status. In gastroenterology, for the correct diagnosis of a number of diseases, for example, the esophagus and stomach, a simultaneous or even average acidity is not significant. Most often, it is important to understand the dynamics of changes in acidity during the day (nighttime acidity often differs from daytime) in several areas of the body. Sometimes it is important to know the change in acidity as a reaction to certain irritants and stimulants.
PH value
In solutions of inorganic substances: salts, acids and alkalis are separated into their constituent ions. In this case, H + hydrogen ions are carriers of acidic properties, and OH - ions are carriers of alkaline properties. In highly diluted solutions, the acid and alkaline properties depend on the concentrations of H + and OH - ions. In ordinary solutions, the acid and alkaline properties depend on the activity of a H and a OH ions, that is, on the same concentrations, but adjusted for the activity coefficient γ, which is determined experimentally. For aqueous solutions, the equilibrium equation applies: a H × a OH \u003d K w, where K w is a constant, the ionic product of water (K \u200b\u200bw \u003d 10 - 14 at a water temperature of 22 ° C). From this equation it follows that the activity of hydrogen ions H + and the activity of OH - ions are interconnected. Danish biochemist S.P.L. Serensen in 1909 proposed a hydrogen show pH, equal by definition to the decimal logarithm of the activity of hydrogen ions taken with a minus (Rapoport S.I. and others):
pH \u003d - log (a N).
Based on the fact that in a neutral medium a Н \u003d а ОН and from the equality for pure water at 22 ° С: а Н × а ОН \u003d К w \u003d 10 - 14, we find that the acidity of pure water at 22 ° С (then there is neutral acidity) \u003d 7 units. pH
Solutions and liquids with respect to their acidity are considered:
- neutral at pH \u003d 7
- acidic at pH< 7
- alkaline at pH\u003e 7
Some misconceptions
If one of the patients says that he has "zero acidity", then this is nothing more than a speech turn, meaning, most likely, that he has a neutral value of acidity (pH \u003d 7). In the human body, the value of the acidity index cannot be less than 0.86 pH. It is also a common misconception that acidity values \u200b\u200bcan only be in the range from 0 to 14 pH. Acidity and negative are possible in technology, and more than 20.When talking about the acidity of an organ, it is important to understand that often in different parts of an organ, acidity can vary significantly. The acidity of the contents in the lumen of the organ and the acidity on the surface of the mucous membrane of the organ are also often not the same. For the mucous membrane of the body of the stomach, it is characteristic that the acidity on the surface of the mucus facing the lumen of the stomach acidity is 1.2-1.5 pH, and on the side of the mucus facing the epithelium is neutral (7.0 pH).
PH for some foods and water
The table below shows the acidity values \u200b\u200bof some common products and pure water at different temperatures:| Product | Acidity pH |
| Lemon juice | 2,1 |
| Wine | 3,5 |
| Tomato juice | 4,1 |
| Orange juice | 4,2 |
| Black coffee | 5,0 |
| Pure water at 100 ° C |
6,13 |
| Pure water at 50 ° C |
6,63 |
| Fresh milk | 6,68 |
| Pure water at 22 ° C |
7,0 |
| Pure water at 0 ° С | 7,48 |
Acidity and Digestive Enzymes
Very many processes in the body are impossible without the participation of special proteins - enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions in the body without being subjected to chemical transformations. The digestive process is not possible without the participation of a variety of digestive enzymes that break down various organic food molecules and act only in a narrow range of acidity (different for each enzyme). The most important proteolytic enzymes (splitting food proteins) of gastric juice: pepsin, gastricin and chymosin (rennin) are produced in an inactive form - in the form of proenzymes and later activated by hydrochloric acid of gastric juice. Pepsin is most active in a strongly acidic environment, with a pH of 1 to 2, gastriksin has a maximum activity at pH 3.0–3.5, chymosin, which breaks down milk proteins to an insoluble casein protein, has a maximum activity at pH 3.0–3.5 .Proteolytic enzymes secreted by the pancreas and “acting” in the duodenum: trypsin having optimum action in a slightly alkaline medium, at pH 7.8–8.0, and chymotrypsin, which is closest to it in functionality, is most active in an environment with acidity up to 8.2. The maximum activity of carboxypeptidases A and B is 7.5 pH. Other maximum enzymes that perform digestive functions in a slightly alkaline environment of the intestine have similar maximum values.
Reduced or increased acidity in relation to the norm in the stomach or duodenum, thus, leads to a significant decrease in the activity of certain enzymes or even their exclusion from the digestive process, and as a result to digestive problems.
Acidity of saliva and oral cavity
The acidity of saliva depends on the rate of salivation. Typically, the acidity of mixed human saliva is 6.8–7.4 pH, but at high salivation rates it reaches 7.8 pH. The salivary acidity of the parotid glands is 5.81 pH, submandibular - 6.39 pH.In children, the average acidity of mixed saliva is 7.32 pH, in adults - 6.40 pH (Rimarchuk G.V. et al.).
The acidity of plaque depends on the condition of the hard tissues of the teeth. Being neutral in healthy teeth, it shifts to the acid side, depending on the degree of development of caries and the age of adolescents. In 12-year-olds with an initial stage of caries (pre-caries), plaque acidity is 6.96 ± 0.1 pH, in 12–13-year-olds with an average caries, plaque acidity is from 6.63 to 6.74 pH, in 16 -year-old adolescents with superficial and secondary caries, the acidity of plaque is equal to 6.43 ± 0.1 pH and 6.32 ± 0.1 pH, respectively (Krivonogova LB).
Acidity of the secretion of the pharynx and larynx
The acidity of the secretion of the pharynx and larynx in healthy and patients with chronic laryngitis and pharyngolaryngeal reflux is different (A.V. Lunev):|
Groups surveyed |
PH measurement location |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pharynx, |
Larynx, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Healthy faces |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Patients with chronic laryngitis without GERD |
The figure above shows a graph of acidity in the esophagus of a healthy person, obtained using intragastric pH metering (Rapoport S.I.). Gastroesophageal refluxes are clearly observed on the graph - sharp decreases in acidity to 2-3 pH, which in this case are physiological. Acidity in the stomach. High and low acidity The maximum observed acidity in the stomach is 0.86 pH, which corresponds to an acid production of 160 mmol / L. The minimum acidity in the stomach is 8.3 pH, which corresponds to the acidity of a saturated solution of HCO 3 - ions. Normal acidity in the stomach lumen on an empty stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH. Acidity on the surface of the epithelial layer facing the lumen of the stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH. Acidity in the depths of the epithelial layer of the stomach is about 7.0 pH. Normal acidity in the antrum of the stomach is 1.3–7.4 pH. The maximum observed acidity in the stomach is 0.86 pH, which corresponds to an acid production of 160 mmol / L. The minimum acidity in the stomach is 8.3 pH, which corresponds to the acidity of a saturated solution of HCO 3 - ions. Normal acidity in the stomach lumen on an empty stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH. Acidity on the surface of the epithelial layer facing the lumen of the stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH. Acidity in the depths of the epithelial layer of the stomach is about 7.0 pH. Normal acidity in the antrum of the stomach is 1.3–7.4 pH. The cause of many diseases of the digestive tract is an imbalance in the processes of acid production and acid neutralization. Prolonged hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid or lack of acid neutralization, and, as a result, increased acidity in the stomach and / or duodenum, causes the so-called acid-dependent diseases. At present, they include: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum with aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), gastronasitis E and Zollingerdea syndrome high acidity and others. Reduced acidity is observed with anacid or hypoacid gastritis or gastroduodenitis, as well as with stomach cancer. Gastritis (gastroduodenitis) is called anacid or gastritis (gastroduodenitis) with low acidity, if the acidity in the body of the stomach is about 5 or more units. pH The cause of low acidity is often atrophy of parietal cells in the mucous membrane or a violation in their functions. Above is a graph of acidity (daily pH-gram) of the body of a healthy person’s stomach (dashed line) and of a duodenal ulcer patient (solid line). Meal times are marked with arrows labeled "Food." The graph shows the acid-neutralizing effect of food, as well as the increased acidity of the stomach with duodenal ulcer (Yakovenko A.V.). Intestinal acidityNormal acidity in the duodenal bulb is 5.6–7.9 pH. The acidity in the jejunum and ileum is neutral or slightly alkaline and ranges from 7 to 8 pH. The acidity of the juice of the small intestine is 7.2–7.5 pH. With increased secretion, it reaches 8.6 pH. The acidity of the secretion of the duodenal glands is from pH 7 to pH 8.
Fecal acidityThe acidity of feces of a healthy person eating mixed foods is determined by the vital activity of the colon microflora and is equal to 6.8–7.6 pH. Normal fecal acidity is considered in the range from 6.0 to 8.0 pH. The acidity of meconium (the original feces of newborns) is about 6 pH. Deviations from the norm with fecal acidity:
Blood acidityThe acidity of human arterial blood plasma ranges from 7.37 to 7.43 pH, averaging 7.4 pH. The acid-base balance in human blood is one of the most stable parameters, which maintains the acid and base components in a certain balance within very narrow boundaries. Even a small shift from these limits can lead to severe pathology. With a shift to the acid side, a condition called acidosis occurs, to the alkaline side, alkolosis. Changes in blood acidity above 7.8 pH or below 6.8 pH are incompatible with life.The acidity of venous blood is 7.32-7.42 pH. The acidity of red blood cells is 7.28–7.29 pH. Urine acidityIn a healthy person with a normal drinking regime and a balanced diet, the acidity of urine is in the range from 5.0 to 6.0 pH, but can range from 4.5 to 8.0 pH. The acidity of the urine of a newborn under the age of one month is normal - from 5.0 to 7.0 pH.Urine acidity increases if protein-rich meat predominates in the human diet. Increases the acidity of urine hard physical work. Milk and vegetable diet leads to the fact that urine becomes slightly alkaline. An increase in the acidity of urine is noted with increased acidity of the stomach. Reduced acidity of gastric juice does not affect the acidity of urine. A change in urine acidity most often corresponds to a change. Urine acidity changes with many diseases or conditions of the body, so the determination of urine acidity is an important diagnostic factor. Vaginal acidityThe normal acidity of a woman’s vagina ranges from 3.8 to 4.4 pH and averages 4.0–4.2 pH. Vaginal acidity in various diseases:
Publications for Health Professionals on Acidity in the Female Genital Organs
Sperm acidityNormal sperm acidity ranges from 7.2 to 8.0 pH. Deviations from these values \u200b\u200bare not per se considered pathological. At the same time, together with other deviations may indicate the presence of the disease. An increase in sperm pH occurs during the infectious process. A sharp alkaline reaction of sperm (acidity of about 9.0-10.0 pH) indicates pathology of the prostate gland. When the excretory ducts of both seminal vesicles are blocked, an acidic sperm reaction is observed (acidity 6.0–6.8 pH). The fertilizing ability of such sperm is reduced. In an acidic environment, sperm lose their motility and die. If the acidity of the seminal fluid becomes less than 6.0 pH, the sperm cells completely lose their mobility and die.Skin acidityThe surface of the skin is coated with water-lipid acid mantle or marchionini mantle, consisting of a mixture of sebum and sweat, in which organic acids are added - lactic, citric and others, formed as a result of biochemical processes in the epidermis. The acidic water-lipid mantle of the skin is the first barrier to protection against microorganisms. In most people, the normal acidity of the mantle is 3.5–6.7 pH. The bactericidal property of the skin, which gives it the ability to withstand microbial invasion, is due to the acid reaction of keratin, a peculiar chemical composition of sebum and sweat, and the presence of a protective water-lipid mantle with a high concentration of hydrogen ions on its surface. Its low molecular weight fatty acids, primarily glycophospholipids and free fatty acids, have a bacteriostatic effect that is selective for pathogenic microorganisms. The skin surface is populated by a normal symbiotic microflora, capable of existing in an acidic environment: Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Propionibacterium acnes other. Some of these bacteria themselves produce lactic and other acids, contributing to the formation of the acid mantle of the skin.The upper layer of the epidermis (keratin flakes) has an acidity with a pH from 5.0 to 6.0. With some skin diseases, the amount of acidity changes. For example, with fungal diseases, the pH rises to 6, with eczema to 6.5, with acne to 7. Acidity of other human biological fluidsThe acidity of fluids within the human body normally coincides with the acidity of the blood and ranges from 7.35 to 7.45 pH. The acidity of some other human biological fluids is normally shown in the table:On the right photo: buffer solutions with pH \u003d 1.2 and pH \u003d 9.18 for calibration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
pH is a measure of the relative acidity or alkalinity of a solution. A pH of 7 is considered a neutral solution, acidic solutions are below 7 and alkaline are above 7. The pH can be measured with a pH meter, a portable pH meter, or with a litmus test. PH measurement provides a numerical indication of relative acidity or alkalinity, which is an important parameter in the control solution.
In order for the solution to perform its functions as necessary, the desired pH must be known, and then the solution can be controlled. To illustrate, consider the production of jelly. To turn fruit into jelly, the mixture should be slightly acidic. At a pH below 2.6, the mixture will not turn into jelly; at a value of 2: 6, a white precipitate forms, and the jelly does not have a market appearance; at a value of 2.8, water droplets are separated from the mixture; at a value of 3.1, the mixture forms a jelly of maximum consistency; at a value of 3.2, a jelly of medium consistency is formed, and at 3.3, the jelly will be liquid. If the pH is above 3.5 jelly, the mixture does not work out at all.
So, within a few tenths of the pH, no jelly is formed from the mixture, then the maximum consistency is obtained, then the jelly is not obtained again. This example illustrates the importance of tight control of the pH of a solution.
There is a wide range of acids, from sulfuric acid, which can dissolve metal to boric acid, which is suitable for washing the eyes. All acids form hydrogen ions (H +) in solution. The degree of acidity is a numerical designation of the concentration of hydrogen ions. In the language of chemistry, the numerical designations of the concentration of hydrogen ions are usually extremely small fractions, for example, 1/10 000 000. The pH scale was designed to avoid the use of such inconvenient numbers. The pH scale is defined mathematically as the negative logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions or the degree to which 10 should be raised to equal the concentration of hydrogen ions. The name pH comes from the term "degree of hydrogen." The mathematical expression provides us with a convenient scale from 0 for an acid solution of specific strength to 7 for a neutral solution of pure water.
Alkalis owe their alkalinity to hydroxyl ions (OH-), which they form in solution. Alkalinity can be measured on the same scale as acidity, from 7 to 14.
Simply put, any number below 7.0 is an acid, and with each unit of decrease in this value, the intensity (ion concentration of H +) of the acid increases by a factor of 10X. Any number above 7.0 is considered alkali, and for each unit of increase in this value, the intensity (ionic concentration of OH-) of alkali increases by a factor of 10X. In a solution where the same amount of H + ions and OH- ions are present, the pH is 7.0.
Tap water may be slightly alkaline due to the addition of caustic soda to make the water more enjoyable to drink. Proper measurement and regulation of water is essential in the pre-treatment process. To ensure accurate measurements, the pH meter must be properly calibrated.
Single point calibration is described below.
1) Connect the pH electrode to the device and remove the protective cap from the electrode.
2) Wash the pH electrode with distilled water and immerse it in 7.00 buffer solution. *
3) Turn on the device by setting the three-position switch to the ON position.
4) Set the temperature control of the instrument to the temperature of the buffer solution (use a Tru GT 100R thermometer or other suitable thermometer to measure the temperature of the buffer solution).
5) Adjust the standardization control to read the value corresponding to the temperature of the buffer solution. Buffer values \u200b\u200bare given in Table 1.
6) Remove the electrode from the buffer solution and rinse with distilled water.
The pH meter is now calibrated and ready for use.
The temperature control button on the device must be set to the temperature of the solution, the pH value of which is measured.
The electrode must not be allowed to dry. If not used, the electrode should be immersed in a buffer solution. The electrode should not be used in solutions with temperatures above 140 ° F (60 ° C) and should be protected from freezing. The electrode should be washed with distilled water before being transferred to the buffer solution from the measured solution. The moisture from the electrode must be shaken off to reduce the contamination of the solution when transferring the electrode from one solution to another.
If a film coating forms on the tip of the electrode, try to remove it by actively interfering in the washing solution or pollinating it from the spray can. If this does not work, and the device responds slowly or incorrectly, you can gently clean the glass vessel with a soft brush. If this does not work, replace the vessel or device.
The pH values \u200b\u200bof the buffers should be checked periodically by comparing them with the values \u200b\u200bin fresh buffers. Replace the solution when the pH difference reaches 0.1 or more.
One of the most important properties of aqueous solutions is their acidity (or alkalinity), which is determined by the concentration of H ions + and OH - ( cm . ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION. ELECTROLYTES) The concentrations of these ions in aqueous solutions are related by a simple dependence \u003d TO w ; (square brackets are used to denote the concentration in units of mol / l). The value of Kw is called the ionic product of water and is constant at a given temperature. So, at 0 about С, it is 0.11 С 10 –14, at 20 о С - 0.69 С 10 –14, and at 100 о С - 55.0 С 10 –14 . Most commonly used valueK w at 25 about C, which is 1.00Ch 10-14 . In absolutely pure water, not even containing dissolved gases, the concentration of H ions + and OH - equal (the solution is neutral). In other cases, these concentrations do not coincide: in acid solutions, H ions prevail + , in alkaline - OH ions . But their product in any aqueous solution is constant. Therefore, if you increase the concentration of one of these ions, the concentration of the other ion will decrease by the same amount. So, in a weak acid solution, in which \u003d 10 –5 mol / L, \u003d 10 –9 mol / l, and their product is still equal to 10 –14 . Similarly, in an alkaline solution at \u003d 3.7 × 10 –3 mol / L \u003d 10 –14 / 3.7 × 10 –3 \u003d 2.7 × 10 –11 mol / lFrom the foregoing it follows that the acidity of the solution can be unambiguously expressed by indicating the concentration of only hydrogen ions in it. For example, in pure water \u003d 10 –7 mol / l In practice, operating with such numbers is inconvenient. In addition, the concentration of H ions +
in solutions can vary hundreds of trillions of times - from about 10 –15 mol / l (strong alkali solutions) up to 10 mol / l (concentrated hydrochloric acid), which cannot be shown on any graph. Therefore, it has long been agreed for the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution to indicate only an exponent of 10 taken with the opposite sign; for this, the concentration should be expressed as a degree of 10x, without a multiplier, for example, 3.7H 10 –3 \u003d 10 –2.43 . (In more accurate calculations, especially in concentrated solutions, their activity is used instead of the concentration of ions.) This exponent is called the hydrogen exponent, and the abbreviated pH - from the notation for hydrogen and the German word Potenz - mathematical degree. Thus, by definition, pH \u003d –lg [N +
]; this value can vary within small limits - only from –1 to 15 (and more often from 0 to 14). In this case, the change in the concentration of ions H +
10 times corresponds to a change in pH per unit. The pH designation was introduced into scientific use in 1909 by the Danish physicist and biochemist S.P. L. Sørensen, who at that time was studying the processes that occur during the fermentation of beer malt and their dependence on the acidity of the medium. At room temperature in neutral solutions, pH \u003d 7, in acidic solutions, pH 7. Approximately the pH value of an aqueous solution can be determined using indicators. For example, methyl orange at pH 4.4 is yellow; litmus at pH 8 - blue, etc. More precisely (up to hundredths), the pH value can be determined using special instruments - pH meters. Such devices measure the electric potential of a special electrode immersed in a solution; this potential depends on the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, and it can be measured with high accuracy. It is interesting to compare the pH values \u200b\u200bof solutions of various acids, bases, salts (at a concentration of 0.1 mol / l), as well as some mixtures and natural objects. For sparingly soluble compounds marked with an asterisk, the pH of saturated solutions is shown. Table 1. Hydrogen indicators for solutions Natural water always has an acid reaction (pH 2 + Н 2 О “Н + + НСО 3 2– . If you saturate water with carbon dioxide at atmospheric pressure, the pH of the resulting "soda" will be equal to 3.7; approximately 0.0007% hydrochloric acid has such acidity - gastric juice is much more acidic! But even if you increase the pressure of CO 2
above the solution up to 20 atm, the pH value does not fall below 3.3. This means that carbonated water (in moderation, of course) can be drunk without harm to health, even if it is saturated with carbon dioxide. Certain pH values \u200b\u200bare extremely important for the life of living organisms. Biochemical processes in them should proceed at strictly specified acidity. Biological catalysts - enzymes are able to work only within certain pH ranges, and when these limits are exceeded, their activity can sharply decrease. For example, the activity of the pepsin enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of proteins and thus promotes the digestion of protein foods in the stomach, is maximum at pH values \u200b\u200bof about 2. Therefore, for normal digestion, it is necessary that the gastric juice has fairly low pH values: normal 1.53–1, 67. With gastric ulcer, the pH decreases on average to 1.48, and with a duodenal ulcer it can even reach 105. The exact pH value of gastric juice is determined by intragastric examination (pH probe). If a person has low acidity, In the cells of the body, the pH is about 7, in the extracellular fluid - 7.4. Nerve endings that are outside the cells are very sensitive to changes in pH. With mechanical or thermal damage to tissues, cell walls are destroyed and their contents enter the nerve endings. As a result, a person feels pain. The Scandinavian researcher Olaf Lindahl did this experiment: using a special needleless injector, a very thin stream of solution was injected through the skin of a person, which did not damage the cells, but acted on the nerve endings. It was shown that it is precisely hydrogen cations that cause pain, and with a decrease in the pH of the solution, the pain intensifies. Likewise, a solution of formic acid, which stinging insects or nettles inject under the skin, directly “acts on the nerves”. The different pH of the tissues also explains why with some inflammations a person feels pain, and with some - not. Interestingly, injecting clean water under the skin gave particularly severe pain. This strange at first glance phenomenon is explained as follows: when in contact with clean water, cells break as a result of osmotic pressure and their contents act on nerve endings. In a very narrow range, the pH of the blood should remain; even its slight acidification (acidosis) or alkalization (alkalosis) can lead to the death of the body. Acidosis is observed in diseases such as bronchitis, circulatory failure, lung tumors, pneumonia, diabetes, fever, damage to the kidneys and intestines. Alkolosis is observed with hyperventilation of the lungs (or by inhaling pure oxygen), with anemia, CO poisoning, hysteria, a brain tumor, excessive consumption of drinking soda or alkaline mineral waters, and diuretic drugs. It is interesting that the pH of arterial blood should normally be in the range of 7.37–7.45, and venous - 7.34–7.43. Various microorganisms are also very sensitive to the acidity of the medium. So, pathogenic microbes quickly develop in a slightly alkaline environment, while they cannot withstand an acidic environment. Therefore, for preservation (pickling, salting) products are used, as a rule, acidic solutions, adding vinegar or food acids to them. The correct selection of pH is also of great importance for chemical-technological processes. It is possible to maintain the desired pH value, to prevent it from deviating noticeably in one direction or another when the conditions change, using the so-called buffer (from the English buff - to soften tremors) solutions. Such solutions are often a mixture of a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt. Such solutions "resist" within certain limits (which are called buffer capacity) Many natural fluids have buffering properties. An example is water in the ocean, the buffering properties of which are largely due to dissolved carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon ions of the NSO Cellular fluid, blood are also examples of natural buffers. So, the blood contains about 0.025 mol / L of carbon dioxide, and its content in men is about 5% higher than in women. The concentration of bicarbonate ions in blood is about the same (there are also more of them in men). In soil testing, pH is one of the most important characteristics. Different soils can have a pH from 4.5 to 10. By the pH value, in particular, one can judge the nutrient content in the soil, as well as which plants can grow successfully on this soil. For example, the growth of beans, lettuce, blackcurrant is difficult when the soil pH is below 6.0; cabbage - below 5.4; apple trees - below 5.0; potatoes - below 4.9. Acidic soils are usually less rich in nutrients, because they hold the metal cations necessary for plants worse. For example, hydrogen ions trapped in the soil displace bound Ca For deoxidation of acidic soils, their liming is used - the introduction of substances that gradually bind excess acid. Natural minerals such as chalk, limestone, dolomite, as well as lime, slag from metallurgical plants can serve as such a substance. The amount of deoxidant added depends on the buffer capacity of the soil. For example, liming clay soil requires more deoxidizing agents than sand. Of great importance are the measurements of the pH of rainwater, which can be quite acidic due to the presence of sulfuric and nitric acids in it. These acids are formed in the atmosphere from oxides of nitrogen and sulfur (IV), which are emitted from the wastes of numerous industries, vehicles, boiler houses and thermal power plants. It is known that acid rains with a low pH (less than 5.6) destroy vegetation, the living world of water bodies. Therefore, the pH of rainwater is constantly monitored.
The table allows you to make a number of interesting observations. PH values, for example, immediately show the comparative strength of acids and bases. One can also clearly see the strong change in the neutral medium as a result of hydrolysis of salts formed by weak acids and bases, as well as during the dissociation of acid salts.
Solution
PH
Hcl
1,0
H 2 SO 4
1,2
H 2 C 2 O 4
1,3
NaHSO 4
1,4
H 3 RO 4
1,5
Gastric juice
1,6
Wine acid
2,0
Lemon acid
2,1
HNO 2
2,2
Lemon juice
2,3
Lactic acid
2,4
Salicylic acid
2,4
Table vinegar
3,0
Grapefruit juice
3,2
CO 2
3,7
Apple juice
3,8
H 2 s
4,1
Urine
4,8–7,5
Black coffee
5,0
Saliva
7,4–8
Milk
6,7
Blood
7,35–7,45
Bile
7,8–8,6
Water of the oceans
7,9–8,4
Fe (OH) 2
9,5
MgO
10,0
Mg (OH) 2
10,5
Na 2 CO 3
11
Ca (OH) 2
11,5
NaOH
13,0
Dobish. Electrochemical constants
. M., 1980
Chirkin A. et al. Therapist's diagnostic guide
. Minsk. 1993






